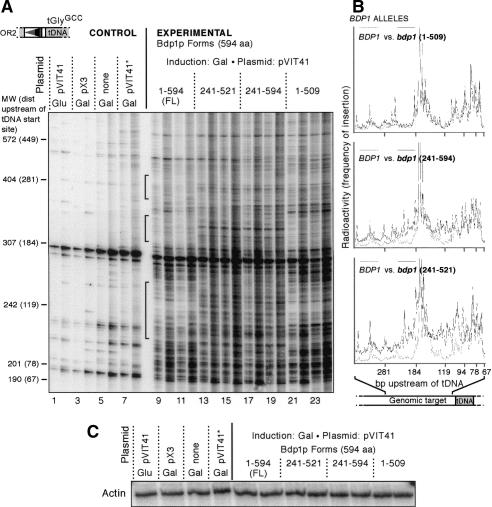
Figure 3.
High-resolution analysis of PCR products from Ty1 integration events in bdp1 mutants. (A) Two transformants per negative control (lanes 1-8) or Bdp1p form (lanes 9-24) were analyzed by PCR. The orientation 2 primer was end-labeled with 32P, and insertions upstream of tGlyGCC genes were analyzed by PCR and run on a 4% polyacrylamide denaturing gel. For each transformant, 28 cycles of PCR (odd-numbered lanes) and 30 cycles of PCR (even-numbered lanes) are shown. Black brackets indicate regions where insertions are seen in the Bdp1p 241-594 and 241-521 mutants but not the full-length Bdp1p. (Glu) No induction on galactose; (pX3) Ty plasmid with no SSB marker in the LTR; (none) no plasmid; (pVIT41★) pVIT41 donor plasmid with a Ty1 element expressing a defective integrase protein; (MW) molecular-weight markers for comparison to size of PCR products on gel. Number in parentheses indicates the relative position upstream of the tDNA transcription start site, which was determined by subtracting the length of the tDNA and the LTR amplified by the OR2 primer (123 bp) from the size of the molecular-weight marker. (B) Traces of the polyacrylamide gel. Radioactivity is plotted vs. distance upstream of the tDNA start site. The trace from full-length Bdp1p (dashed line, trace of lane 9) is compared with Bdp1p 1-509 (top panel, solid line, trace of lane 21), Bdp1p 241-594 (middle panel, solid line, trace of lane 19), and Bdp1p 241-521 (bottom panel, solid line, trace of lane 13). The amount of radioactivity represents the abundance of a PCR product of a given length, which can also be interpreted as the frequency of insertion into a certain position. (C) Loading control: PCR of actin gene using the genomic DNA used in the integration PCR.