Fig. 4. Fundamentals of neurosurgery skill tasks.
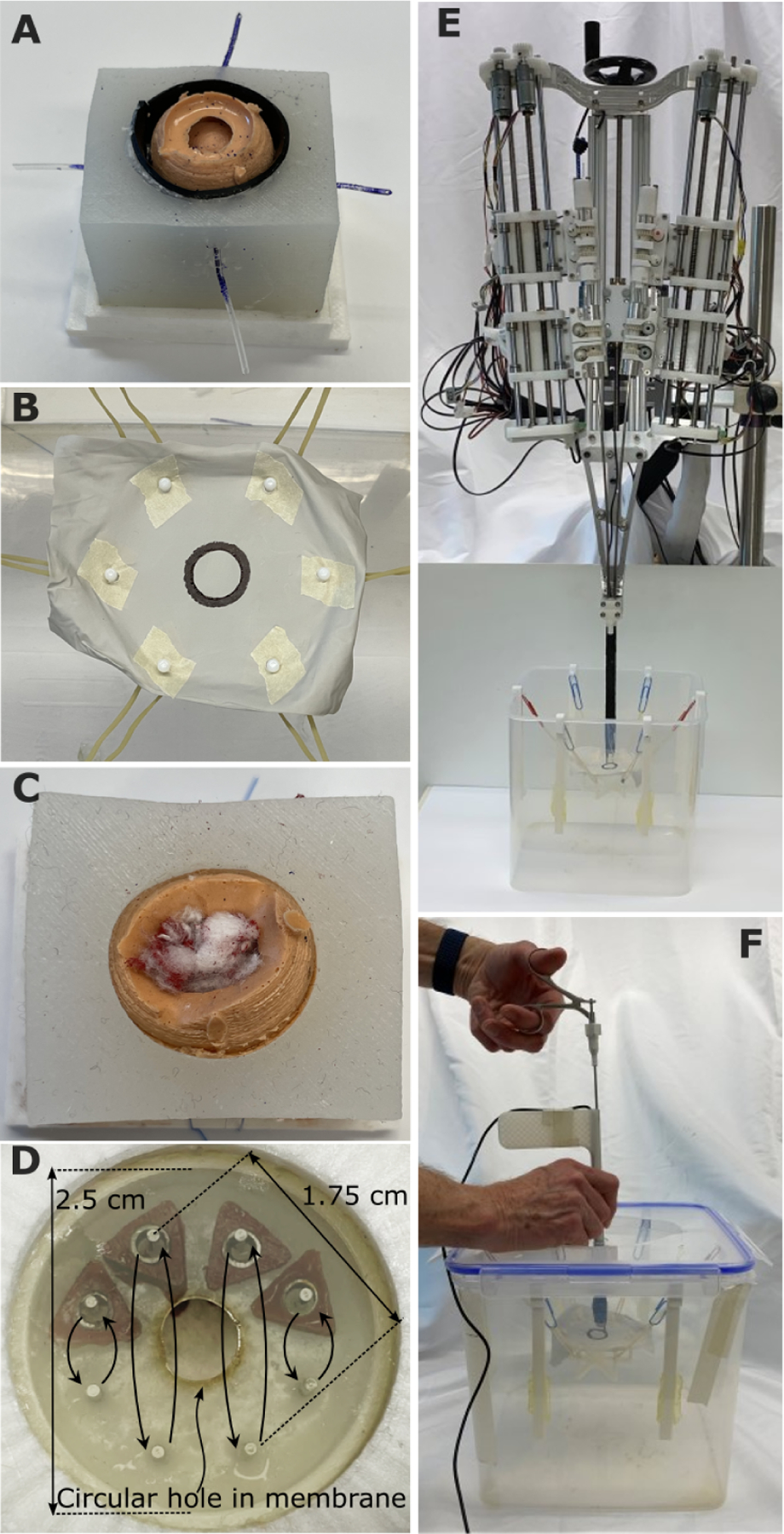
(A) Boundary separation (skill task 1). The goal was to search between the olive-sized tumor and surrounding brain to locate four tubes representing blood vessels. The vessels were first cauterized with forceps and then cut with scissors. The task was to be performed without putting pressure on the surrounding brain surface, composed of a black conductive polymer enabling measurement of tool contact time. This is an inherently bimanual task because one tool is needed to retract the tumor while the second cauterizes and cuts the blood vessel. (B) Capsule cutting (skill task 2). The goal was to cut out a circular window in a polymer sheet while staying inside the black circle boundary. The polymer sheet was mounted on a soft suspension of rubber bands to simulate the compliance of brain tissue. In robotic operation, one arm was used to position and tense the membrane to facilitate cutting by the second arm. (C) Fibrous tumor debulking (skill task 3). The goal was to remove the tumor contents composed of seven small balls of cotton suspended inside the silicone tumor capsule on suture. To remove each ball from its suture attachment, it had to be torn into pieces. In manual operation, each piece was pulled out by the tool through the trocar. In robotic operation, the arms fed the pieces into an aspiration port for removal. (D) Hidden ring transfer (skill task 4). This task evaluated bimanual dexterity and visualization. Four triangular rings and eight pegs were hidden behind an opaque membrane (shown semitransparent here) with a 6 mm–diameter hole in its center. The goal was to move each ring between corresponding top and bottom pegs. In manual operation, the trocar had to be used to pull back the membrane to see the rings and pegs. In robotic operation, one arm could pull back the membrane while the other moved the rings. (E) Robotic skill testing. Robot is positioned above water tank holding each skill task. (F) Manual skill testing. Operator uses manual trocar and tools in identical water tank.
