Fig. 5.
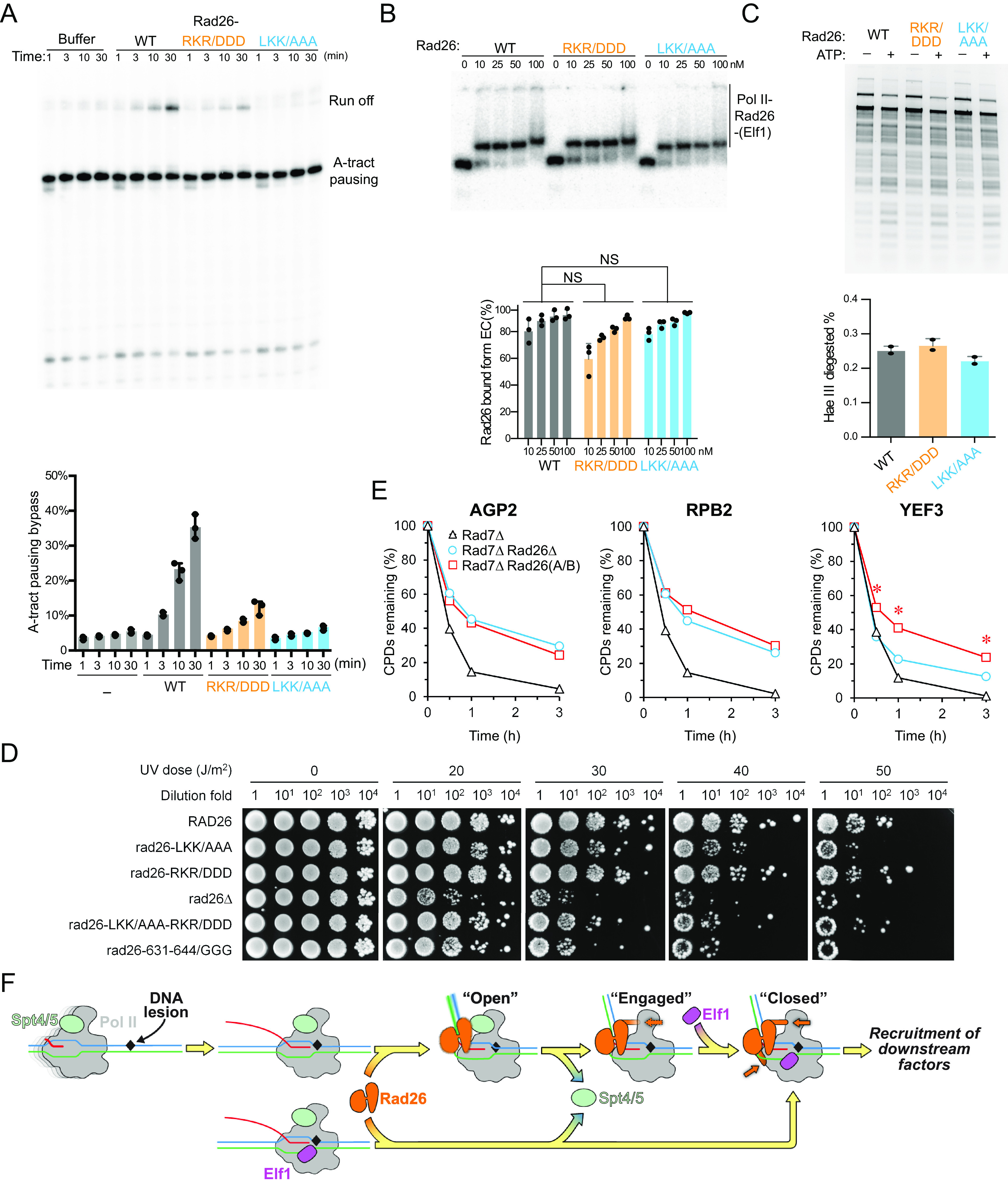
Functional significance of Pol II-Rad26 interface in TC-NER. (A) Rad26 mutants (Rad26-LKK/AAA and Rad26-RKR/DDD) are impaired in promoting Pol II transcription bypass of a pausing sequence. (B) Rad26-LKK/AAA and Rad26-RKR/DDD do not have impaired binding to Pol II. (C) Rad26-LKK/AAA and Rad26-RKR/DDD do not have impaired ATP-dependent DNA translocase activity. All assays in (A–C) were performed at least three times independently. (D) Effects of Rad26 mutations on UV sensitivity. Images are from plates spotted with yeast cells of indicated Rad26 mutations following irradiation with the indicated UV doses. (E) Plots showing the effect of rad26-LKK/AAA-RKR/DDD on TC-NER. The means of percent CPDs remaining at all CPD sites 50 nucleotides downstream of the major transcription start site (TSS) in the template strand of AGP2, RPB2, and YEF3 gens in the indicated cells are plotted. Asterisks (*) indicates that the percent CPDs remaining in the rad7Δ rad26-LKK/AAA-RKR/DDD cells is significantly different from that in the rad7Δ rad26Δ cells at the corresponding repair time points (P values < 10−10, Student’s t test). (F) Stepwise model for lesion recognition and reconfiguration during TC-NER initiation in yeast. The color scheme used in Fig. 5F is as follows: Elf1: magenta, Spt4/5: lime. Other colors are the same as in Fig. 1.
