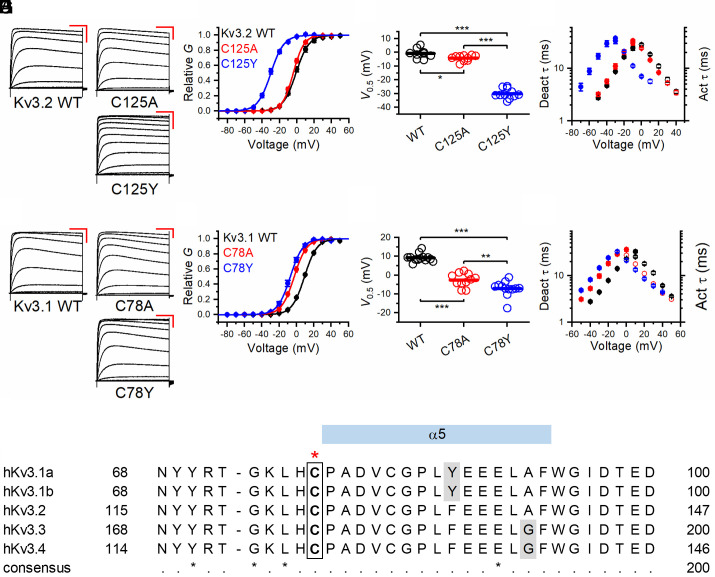
Fig. 3.
Voltage-dependent gating and kinetics of Kv3.2 variants C125A and C125Y and Kv3.1 variants Cys78Ala and Cys78Tyr. (A) Families of whole-oocyte currents of Kv3.2 WT, Cys125Ala (C125A), and Cys125Tyr (C125Y). Currents were evoked by step depolarizations from a holding voltage of −100 mV. The steps were delivered at 10-s intervals in increments of 10 mV. The scale bars are 100 ms and 1 µA, respectively. (B) Normalized peak G-V relations of the indicated Kv3.2 variants. The solid lines represent best-fit first-order Boltzmann functions. (C) Scatter plots of the midpoint voltage (V1/2) determined from the peak G-V relations for the indicated Kv3.2 variants. The horizontal line indicates the mean value. (D) Voltage dependence of the time constants of deactivation (filled symbols) and activation (hollow symbols) for the indicated Kv3.2 variants. (E) Families of whole-oocyte currents of Kv3.1 WT, Cys78Ala, and Cys78Tyr. The protocol and scale bars are as indicated in A. (F) Normalized peak G-V relations of the indicated Kv3.1 variants. The solid lines through the symbols represent best-fit first-order Boltzmann functions. (G) Scatter plots of the midpoint voltage (V1/2) determined from the peak G-V relations for the indicated Kv3.1 variants. The horizontal line indicates the mean value. (H) Voltage dependence of the time constants of deactivation (filled symbols) and activation (hollow symbols) for the indicated Kv3.1 variants. (I) Sequence alignment of human Kv3 family members around the indicated cysteine residue (in the box and highlighted above by the red star). All amino acids are invariant except those indicated by gray shading (which have high sequence conservation). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 via one-way ANOVA.