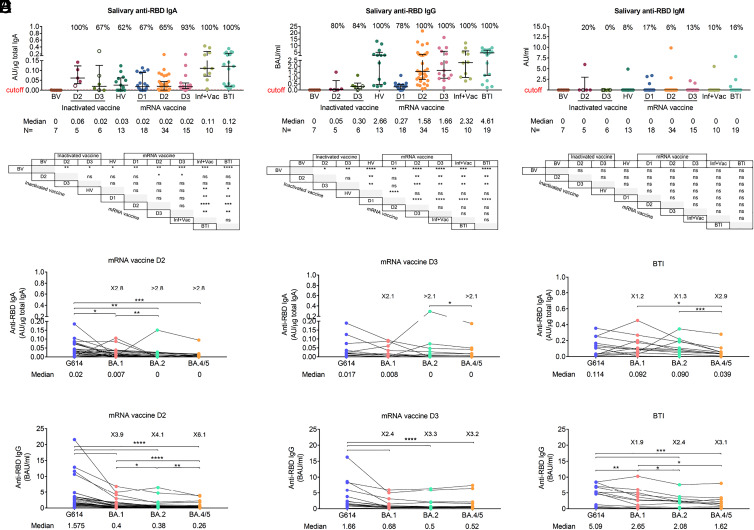
Fig. 1.
Salivary anti-RBD IgA antibodies are produced at low levels following vaccination. (A–C) Salivary anti-RBD IgA (A), IgG (B), and IgM (C) antibodies in different vaccination groups. For each group, the number of samples (n=) and median antibody titers are shown below the x-axis. Whiskers indicate the interquartile range. The results of anti-RBD antibodies are presented as arbitrary units (AU)/µg total IgA (salivary IgA), binding antibody units (BAU/mL) (salivary and plasma IgG) or arbitrary units (AU)/mL (salivary IgM). HV: heterologous vaccination (two doses of inactivated vaccine followed by a heterologous mRNA boost), Inf+Vac: one or two doses of mRNA vaccine after SARS-CoV-2 infection (during the G614 wave), BTI: breakthrough infection (during the BA.1, BA.2, and BA.5 waves) after inactivated and/or mRNA vaccines. A two-sided Mann–Whitney U test was used. (D and E) Salivary anti-RBD IgA (D) and IgG (E) antibodies against G614 and Omicron variants BA.1, BA.2, and BA.4/5 after the second (D2) and third (D3) doses of mRNA vaccine and following BTI in mRNA-vaccinated individuals. In A–E, samples were collected 5 to 59 d (median day 20) after each mRNA dose including after mRNA heterologous boost, 6 to 92 d (median day 51) after doses 2 and 3 of inactivated vaccine, and 8 to 43 d (median day 19) after BTI. The number of fold differences of the median compared to G614 are indicated. A Wilcoxon paired-sample signed-rank test was used. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. ns, not significant. See also SI Appendix, Fig. S1.