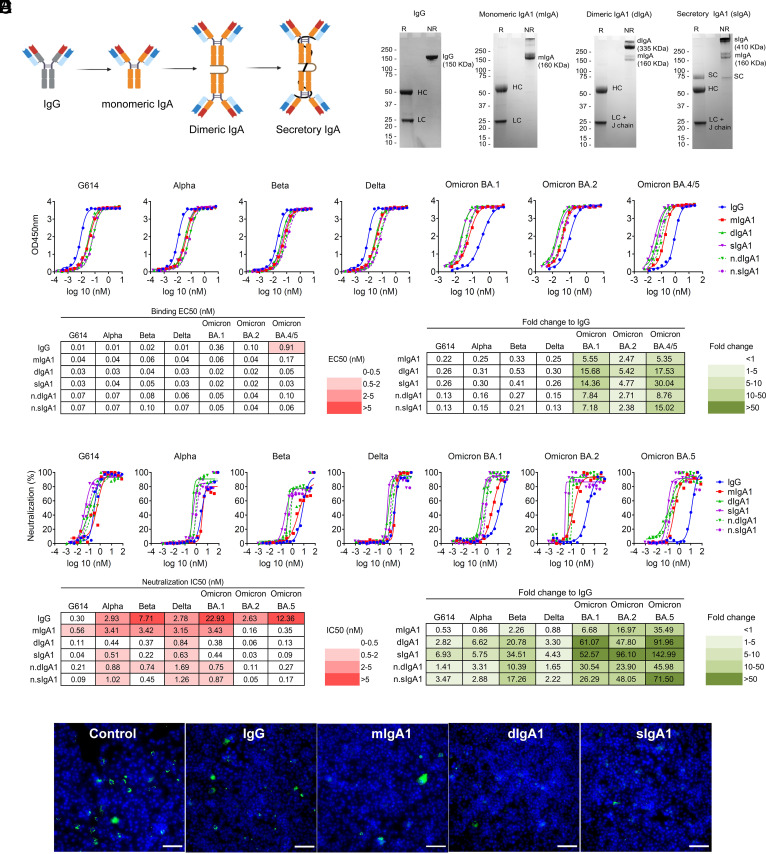
Fig. 3.
Dimeric and secretory IgA1 showed enhanced binding and neutralization activity against VOCs. (A) Illustration showing antibodies engineered from IgG into monomeric, dimeric, and secretory IgA1. (B) SDS–PAGE under reducing (R) and nonreducing (NR) conditions showing the assembly and purity of DXP-604 IgG and IgA1 antibodies. HC, heavy chain; LC, light chain; SC, secretory component; J chain, joining chain. The J chain migrates at the same molecular weight as the light chain. (C and D) Binding to RBD (C) and neutralization (D) of G614 and VOCs by DXP-604 IgG and IgA [monomeric (mIgA1), dimeric (dIgA1), and secretory IgA1 (sIgA1)] antibodies. The EC50 and IC50 and fold-change differences between IgG and IgA1 antibody forms are indicated. n.dIgA1 and n.sIgA1 represent normalized values according to the number of binding sites. (E) Staining of virus following infection of Vero E6 cells with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 preincubated with 3.3 nM DXP-604 IgG or IgA1 forms. Omicron BA.1-infected cells were used as a negative control (control). SARS-CoV-2 virus was visualized using Alexa 488 (green)-conjugated antibody, and the nucleus was stained with DAPI (blue). (Scale bar, 100 μM.) See also SI Appendix, Figs. S5 and S6.