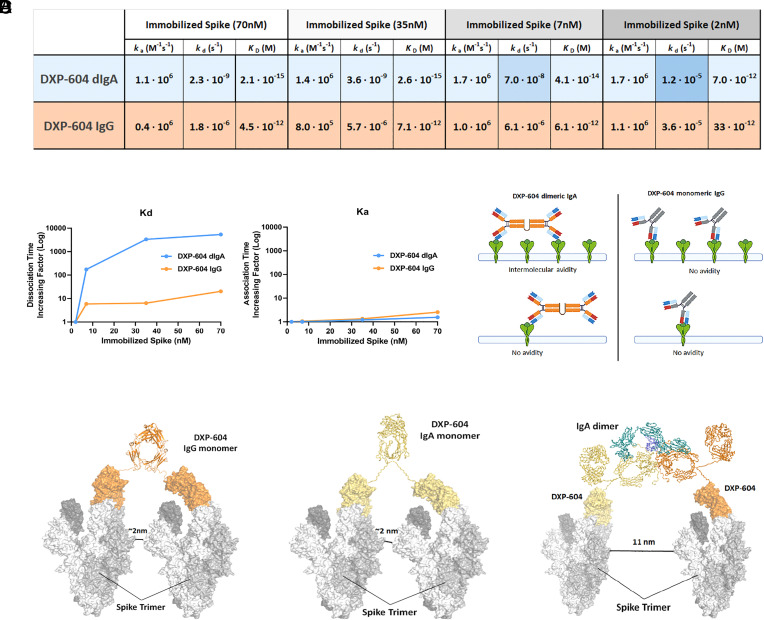
Fig. 4.
Increased neutralization potency of DXP-604 dimeric IgA is associated with increased avidity. (A) ka/kd values obtained at different concentrations of immobilized antigen (Spike) for DXP-604 dimeric IgA1 and IgG forms. ka remains equal across concentrations whereas kd becomes ~1,000 times slower for the dIgA1, indicative of intermolecular avidity available only to the dIgA1. Shades of blue indicate the difference in kd value for DXP-604 dIgA1. (B) Plots of kd (Left) and ka (Right) at different concentrations of immobilized spike, highlighting intermolecular avidity effects (slower dissociation, same association) for the dIgA1 (blue) in comparison to the IgG (orange). (C) DXP-604 dIgA1 and monomeric IgG have different binding modes that are available when high or low quantities of S-trimers are immobilized on the surface of the SPR chip. (D) Computational simulation showing inter-Spike linking by DXP-604 monomeric IgG and IgA1, and dimeric IgA1 antibodies. The predicted distance between S-trimers necessary for interlinking is indicated.