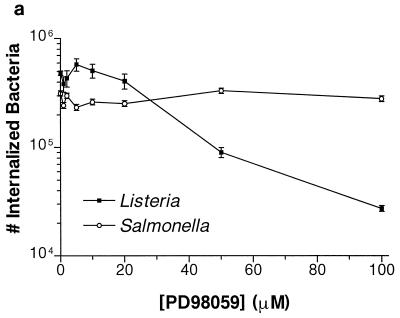
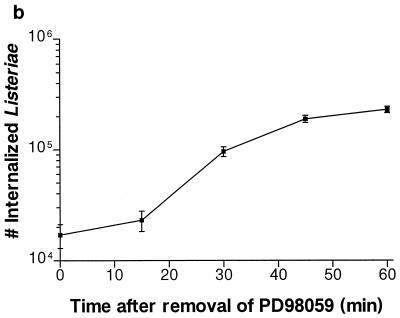
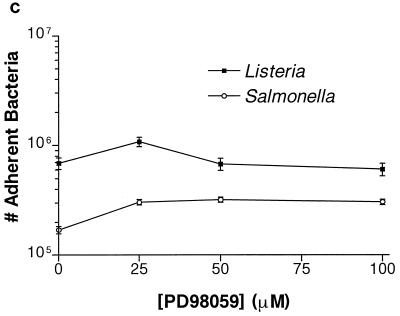
FIG. 1.
Effect of PD98059 on Listeria and Salmonella invasion into HeLa cells. HeLa cells were pretreated for 60 min with various concentrations of PD98059 prior to bacterial infection. Appropriate amounts of the solvent DMSO were added so that all wells contained equivalent concentrations of DMSO. (a) PD98059 blocks Listeria but not Salmonella invasion into HeLa cells. L. monocytogenes 1/2a3 and S. typhimurium SL1344 were allowed to invade for 60 min and 30 min, respectively, before gentamicin was added to kill extracellular bacteria. (b) Inhibition of L. monocytogenes invasion by PD98059 is reversible. HeLa cells were incubated with 100 μM PD98059 for 60 min. The cells were then infected with L. monocytogenes 1/2a3 for 60 min before the PD98059 was washed away. At various time points after the removal of PD98059, the medium was replaced with 100 μg of gentamicin per ml in MEM to kill extracellular bacteria. (c) PD98059 does not affect adherence of Listeria or Salmonella. L. monocytogenes 1/2a3 was allowed to infect the cells for 45 min, and S. typhimurium SL1344 was allowed to infect for 15 min. Monolayers were washed three times with PBS. Adherent (and some internalized bacteria) were released by the lysis of the cells and were quantitated by plating. For each panel, experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results, and the graph depicts one representative experiment; each data point is the mean of data from three wells, and the standard deviation is shown by the error bar.