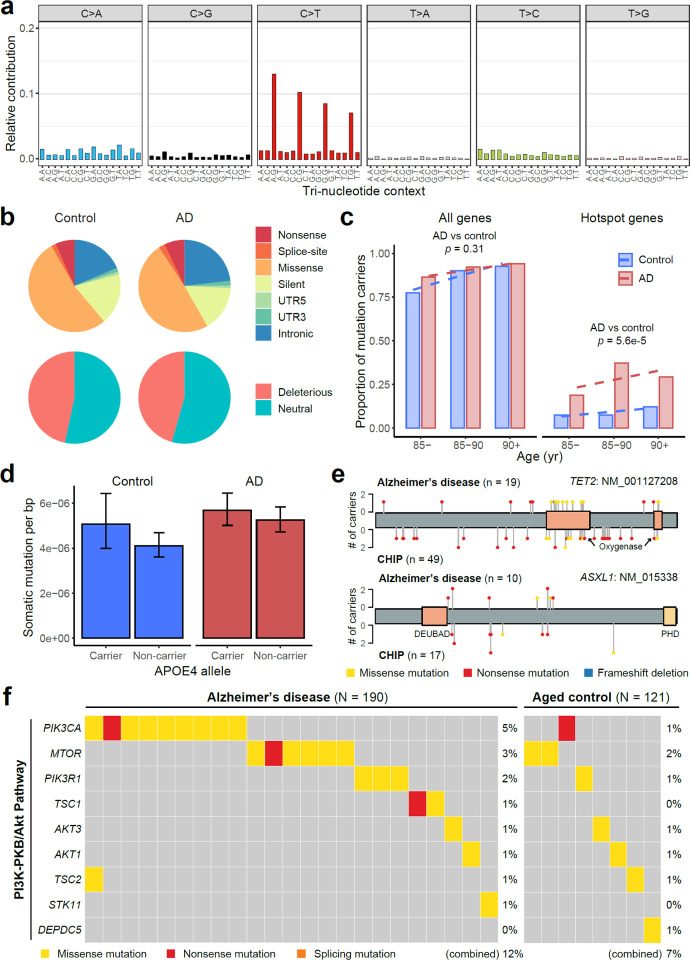
Extended Data Fig. 3. Identification and functional annotation of sSNVs in panel sequencing data.
a, Mutation type and tri-nucleotide context of sSNVs. b, Genic annotation and functional impact prediction of sSNVs identified from AD and control PFC samples. c, The proportion of somatic mutation carriers increases with age. AD patients had a significantly larger proportion of carriers with somatic mutations in AD hotspot genes than matched controls (p = 5.6e-5, linear regression). d, APOE4 carriers tend to have higher burden of sSNVs than non-carriers in both AD and control groups (p = 0.09, linear regression). e, Similar distributions between somatic mutations identified in AD brains and previously reported CH-associated mutations in blood. f, Genes in the PI3K-PKB/Akt pathway contained significantly more somatic mutations in AD brains (12% of AD samples vs 7% of control samples; p < 0.05, one-tailed proportion test).