Fig 2. Cryo-EM of ACAD11 reveals structural determinants of molecular function.
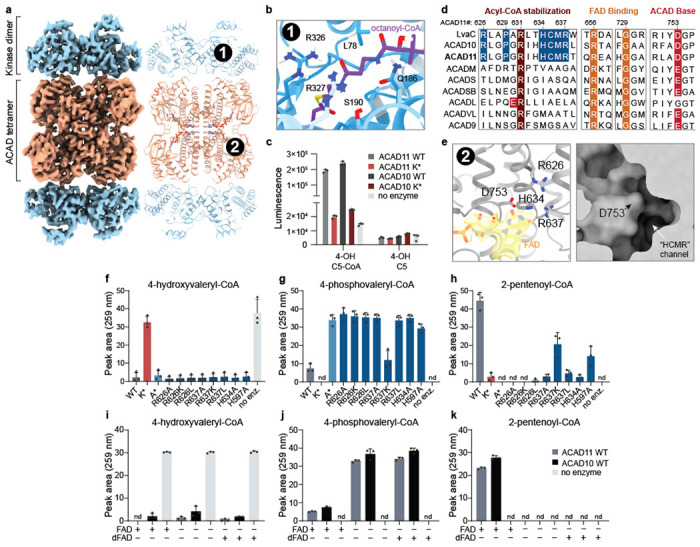
(a) Cryo-EM map and model of the ACAD11 A* mutant tetramer incubated with 4-PV-CoA. The kinase and ACAD domains are colored blue and orange respectively. (b) Ab initio HADDOCK docking of octanoyl-CoA into the kinase domain active site. The pantothenic acid region of the octanoyl-CoA ligand is centered (purple). CONSURF residue conservation scores are shown as a gradient from blue to white, with blue as most conserved for ACAD10/11 and LvaA homologs. Proposed interacting residues, L78, Q186, S190, R326, and R327, are presented as sticks. (c) ADP quantification for reaction mixtures containing ACAD10/11 wild type or mutant with 4-hydroxyvaleryl-CoA or 4-hydroxyvalerate substrate. (d) Sequence alignments for M. musculus ACAD10/11 with P. putida LvaC and other M. musculus ACAD family members. Key, highly conserved residues involved in acyl-CoA stabilization, FAD binding and catalytic activity are highlighted in red and orange. Residues proposed as potential ACAD10/11 functional markers are highlighted in blue. (e) FAD binding site in the structure of the ACAD11 K* mutant with 4-HV-CoA. The FAD model and map are highlighted (yellow). Critical residues in the active site, R626, R637, D753 and H634, are presented as sticks. A surface representation of the ACAD domain active site pocket is shown in the right panel. (f-h) UV-Vis HPLC quantification (259 nm) of 4-hydroxyvaleryl-CoA, 4-phosphovaleryl-CoA, and 2-pentenoyl-CoA in reactions containing ACAD11 wild type and mutants. (i-k) UV-Vis HPLC quantification (259 nm) of 4-hydroxyvaleryl-CoA, 4-phosphovaleryl-CoA, and 2-pentenoyl-CoA in reactions containing 5 μM FAD or 5-deazaFAD (dFAD). All assay data are represented as mean −/+ SD (n = 3 technical replicates).
