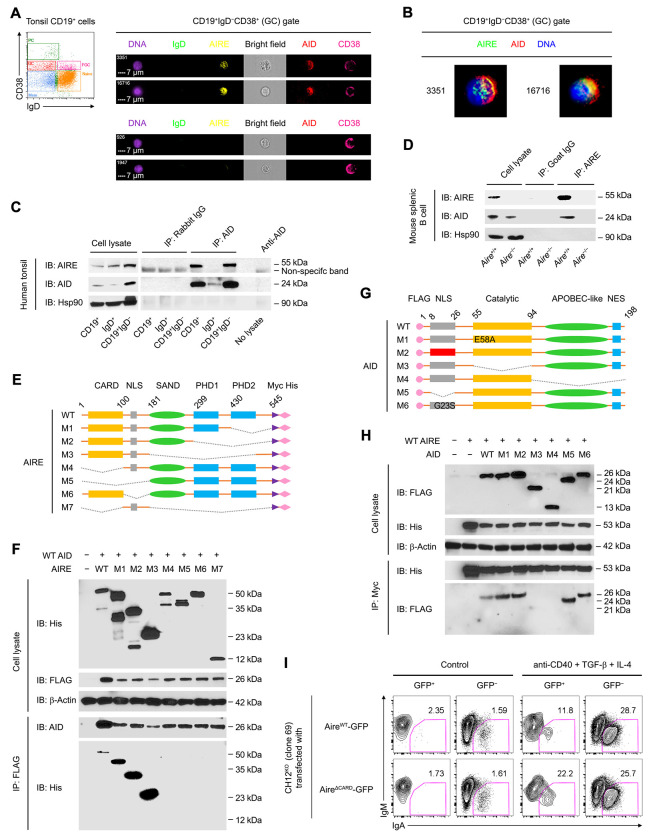
Figure 5. AIRE Interacts with AID in GC B Cells.
(A and B) Imaging flow cytometric analysis of AIRE and AID in tonsillar IgD−CD38+ GC B cells of a healthy donor. Bars: 7 μm (A). The results represent 3 donors.
(C and D) Co-IP of AIRE and AID in tonsillar CD19+ total, IgD+ naive and FGC and CD19+IgD− GC and memory B cells of a healthy donor, and in splenic CD19+ B cells of a B6 mouse after 3 doses of immunization with SRBCs. The results are representative of tonsils of 4 donors and spleens of 3 mice.
(E) The domain structures of recombinant WT and mutant human AIRE and AID molecules. Dotted lines indicated the deleted regions in the mutant proteins.
(F) Co-IP of WT AID and WT or mutant AIRE in HKB-11 cells 24 h after transfection of plasmid(s) encoding WT AID and WT or mutant AIRE proteins.
(G) The domain structures of recombinant WT and mutant human AID proteins.
(H) Co-IP of WT AIRE and WT or mutant AID in HKB-11 cells 24 h after transfection of plasmid(s) encoding WT AIRE and WT or mutant AID proteins. The results in E and G are representative of 3 experiments.
(I) Flow cytometric analysis of IgA CSR in Aire−/− CH12 cells (clone 69) transfected with a plasmid expressing either WT (AireWT-GFP) or CARD-deficient (AireΔCARD-GFP) AIRE-GFP and treated with medium (Control) or anti-CD40, TGF-β and IL-4 for 3 d. The results represent 3 experiments.