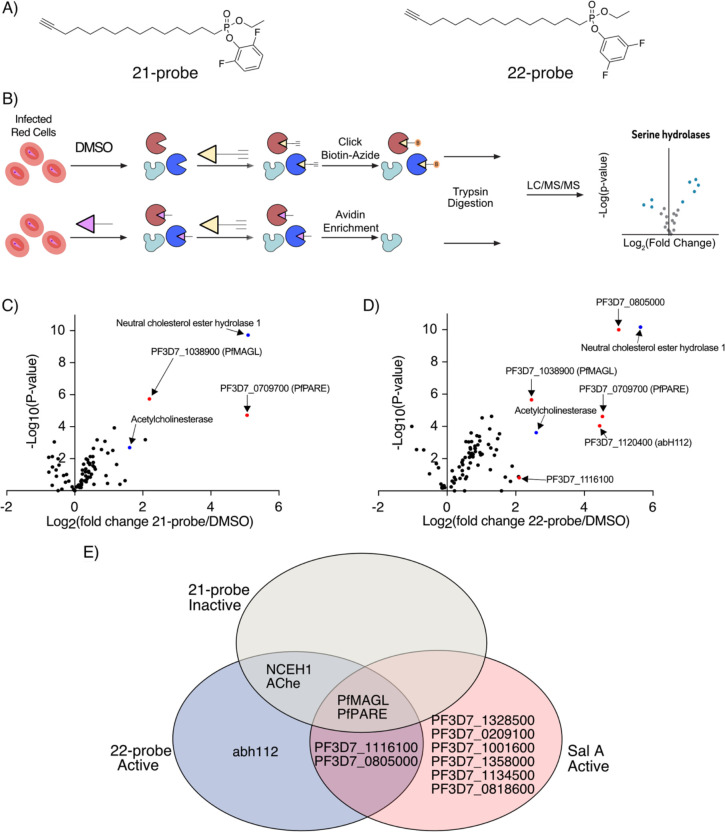
Figure 3: Chemoproteomics identifies distinct serine hydrolases between active and inactive difluorophenol isomers.
(A) Structures of Activity-Based Probes used for chemoproteomics.
(B) Workflow for Competitive ABPP experiment. Infected red bloods are either pretreated with DMSO or the active or inactive inhibitor (green) and followed by treatment with an activity-based probe (orange), before being submitted through typical proteomics workflows.
(C) Volcano plots of Activity-based probe 21-alk targets in P. falciparum. The x axis shows the logarithm values of between 21-alk-treated and DMSO vehicle-treated parasites. The statistical significance was determined without correcting for multiple comparisons in triplicates and the y value in the volcano plot is the negative logarithm of the p value. Significantly enriched serine hydrolases are denoted in red for parasite enzymes and blue for human enzymes.
(D) Volcano plots of Activity-based probe 22-alk targets in P. falciparum. The x axis shows the logarithm values of between 22-alk-treated and DMSO vehicle-treated parasites. The statistical significance was determined without correcting for multiple comparisons in triplicates and the y value in the volcano plot is the negative logarithm of the p value. Significantly enriched serine hydrolases are denoted in red for parasite enzymes and blue for human enzymes.
(E) Venn Diagram showing overlap of significantly enriched serine hydrolases between the inactive probe 21-alk red, the active probe 22-alk, and the natural product Salinipostin A.