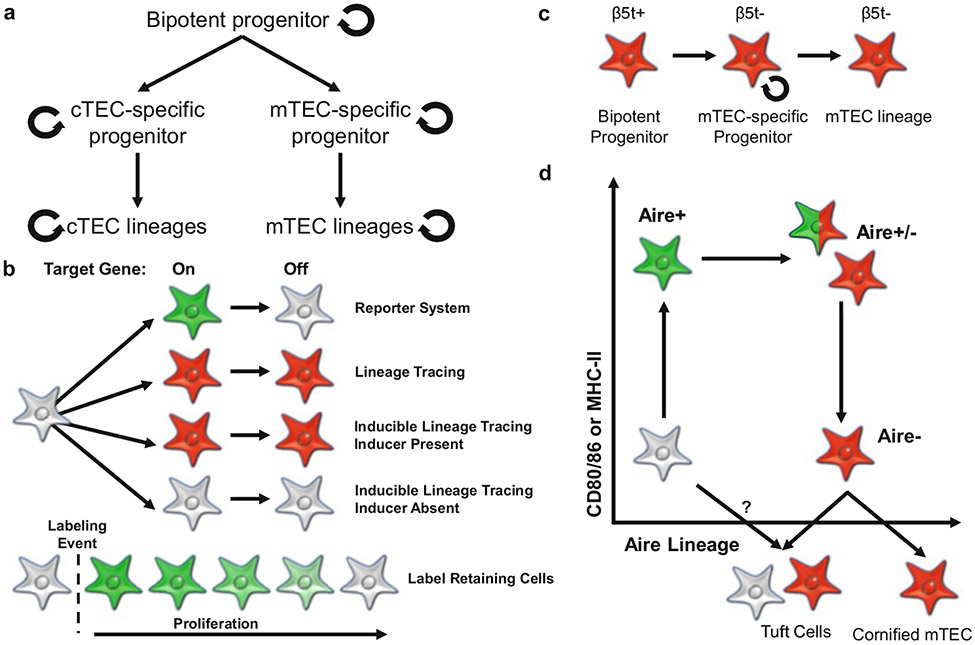
Fig. 3.
The use of lineage tracing to ascertain cellular relationships. (a) Potential models for TEC developmental trajectories and levels of maintenance. (b) The fluorescence phenotypes of reporter (green), lineage tracing (red), and inducible lineage tracing (red) models when the target gene turns on and then off. The fluorescence phenotype of label-retaining cell models with details on before and after the labeling event and the impact of proliferation is also shown. (c) β5t lineage tracing of mTEC development indicates that β5t is expressed in bipotent progenitors and that β5t- mTEC-specific progenitors contribute to the maintenance of the mTEC lineage long term. (d) Combination of Aire-reporter (green) and inducible Aire fate mapping (red) reveals multiple stages of mTEC differentiation. Analysis of a short tamoxifen pulse reveals the presence of Aire-reporter+ and Aire-reporter−, lineage-traced mTEC in the mTEChi fraction, as well as Aire-reporter-, lineage-traced mTEC in the mTEClo fraction. Post-Aire mTEClo cells have been subdivided into cornified mTEC and tuft cells. Lineage tracing has not ruled out the potential for an Aire-independent developmental path for tuft cells