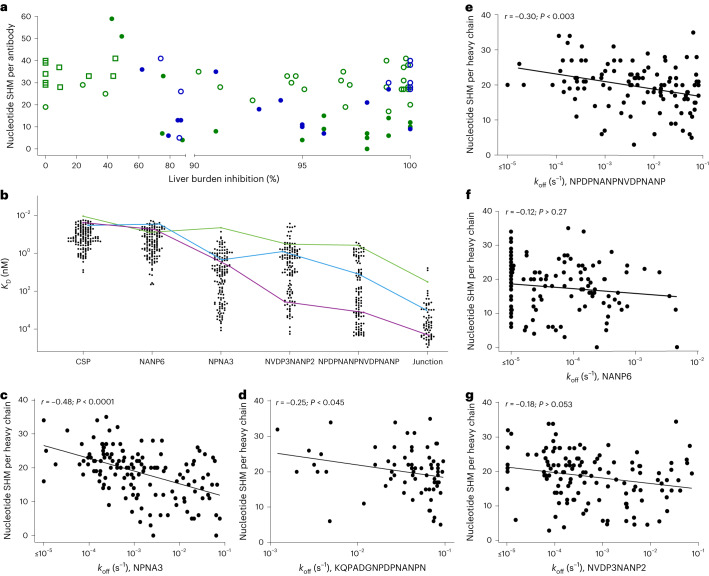
Fig. 2. Functional mAbs bind CSP-derived peptides not present in RTS,S.
a, Percentage inhibition in the sporozoite liver burden mouse model and number of nucleotide mutations from germline are shown for mAbs reactive to either NANP6 repeat-region peptide (circles, n = 67) and C-terminal-region peptide (squares, n = 10), and are indicated as originating from vaccinees who were either protected (green, n = 54) or unprotected (blue, n = 23) and who received either the standard (012M, closed symbols, n = 30) or fractional (Fx017M, open symbols, n = 47) dose. b, SPR-determined binding potencies (Kd) of mAbs (n = 141) selected from 35 of the most efficacious lineages tested against CSP and a panel of CSP-derived peptides that are either homologous (NANP6, NPNA3) or heterologous (NVDP3NANP2, NPDPNANPNVDPNANP, junction [KQPADGNPDPNANPN]) to RTS,S. Examples are shown of a mAb with a broadly promiscuous binding profile (green, AB-007163), another with a profile relatively biased toward homologous peptides (purple, AB-007143) and a third with a profile between these extremes (blue, AB-007175). c–g, Simple two-tailed linear regression comparing the number of nucleotide mutations from germline (SHM) per heavy chain versus log-transformed SPR binding off-rate (koff) against peptides. c, Short, major repeat (NPNA3, n = 140). d, Junctional (KQPADGNPDPNANPN, n = 68). e, Short, minor repeat (NPDPNANPNVDPNANP, n = 109). f, Long, major repeat (NANP6, n = 141). g, Long, minor repeat (NVDP3NANP2, n = 129). See Extended Data Table 1 for correlation analyses with nontransformed data. Dissociation rate (koff) measurements were limited to a minimum of 10−5 s−1. MAbs, with rates ≤10−5 s−1 included in the graphic but excluded from correlation analyses.