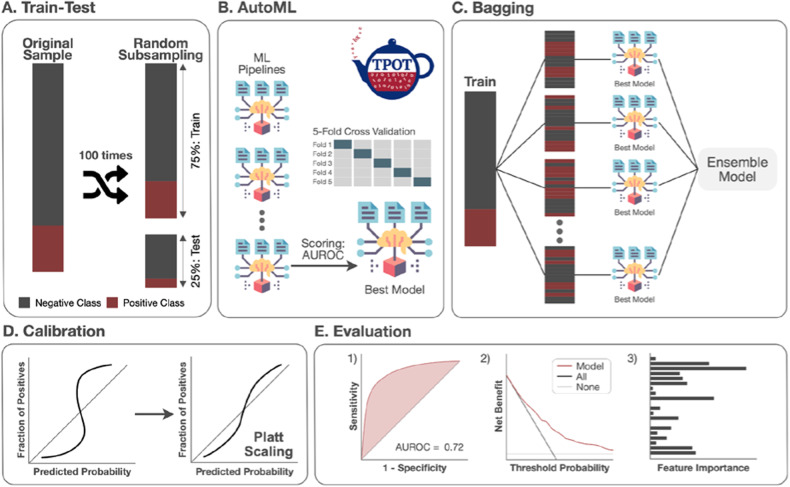
Fig. 1. Overview of probabilistic classification model workflow.
A We split our data using random subsampling. The former approach was the main analysis of the current study. We randomly split the participants into train (75%) and test data sets and repeat this procedure 100 times to obtain a stable performance. The latter approach aims to examine the generalization of our models. B AutoML was implemented in Python using the TPOT package. C Bagging procedure is added when re-training the best model from autoML. D Calibration was performed using Platt scaling. E Evaluation of the performance of test data includes area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), decision curve analysis and feature importance.