Abstract
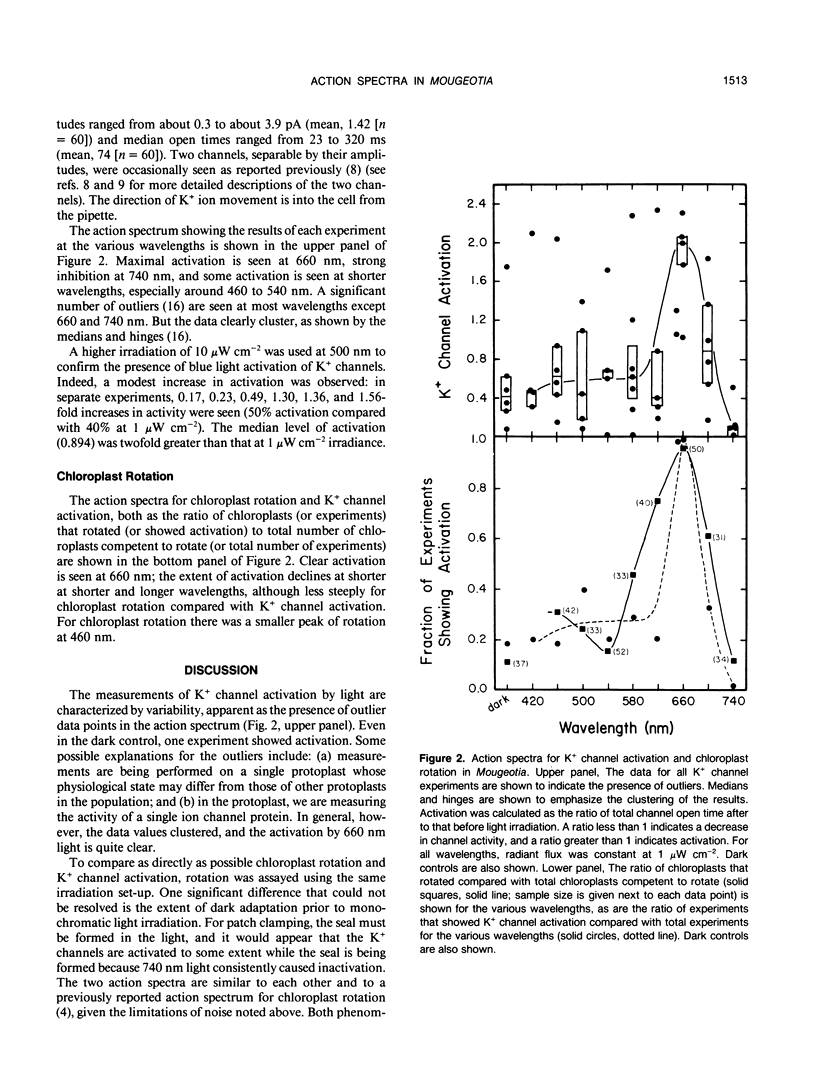
The action spectra for K+ channel activation and chloroplast rotation are shown to be similar. Both phenomena exhibit activation at 660 nanometers, inhibition at 740 nanometers, and partial activation at 460 to 500 nanometers. This confirms that K+ channels in Mougeotia are regulated by phytochrome, and indicates that both phenomena share at least part of the same transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew R. R., Serlin B. S., Schauf C. L., Stockton M. E. Calcium activation of mougeotia potassium channels. Plant Physiol. 1990 Mar;92(3):831–836. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew R. R., Serlin B. S., Schauf C. L., Stockton M. E. Red light regulates calcium-activated potassium channels in mougeotia plasma membrane. Plant Physiol. 1990 Mar;92(3):822–830. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. M., Imakawa K., Niwano Y., Kazemi M., Malathy P. V., Hansen T. R., Glass A. A., Kronenberg L. H. Interferon production by the preimplantation sheep embryo. J Interferon Res. 1989 Apr;9(2):175–187. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serlin B. S., Roux S. J. Modulation of chloroplast movement in the green alga Mougeotia by the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 and by calmodulin antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6368–6372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


