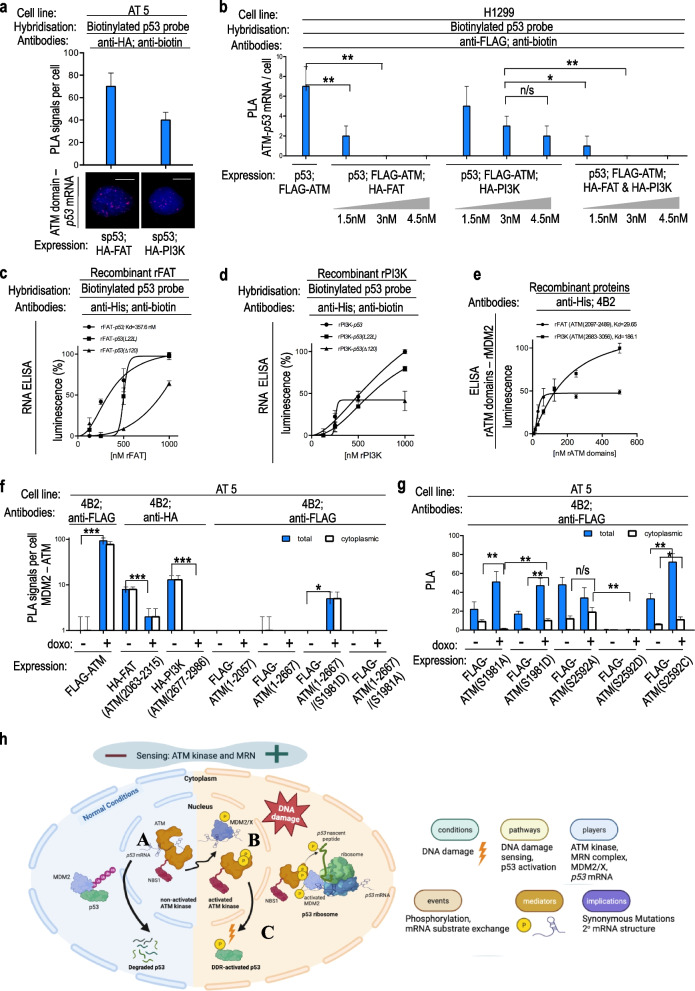
Fig. 2.
a PLA on AT5 BiVA cells (ATM-null), transfected with HA-FAT or HA-PI3K domains of ATM. PLA signal (amount of puncta per cell) shows that both domains independently bind the p53 mRNA, but the FAT domain binds it more prominently. Scale bars represent 10 μm. b PLA on H1299 cells (p53-null), transfected with FLAG-ATM and increasing amounts of HA-FAT or HA-PI3K or both (0, 1.5, 3.0, 4.5 nM). PLA signals show that both FAT and PI3K domains prevent the interaction of the full length ATM with the p53 mRNA in a constitutively manner. c, d Sandwich RNA ELISA using recombinant FAT domain (c) or PI3K domain (d) and in vitro synthesized p53 mRNA (p53wt or p53(L22L) or p53(Δp120)), showing the kinetics of the interactions. The FAT domain shows an increased affinity for the p53 mRNA compared to the PI3K domain. e Sandwich ELISA using his-tagged recombinant FAT domain or PI3K domain proteins with recombinant MDM2 protein. The FAT domain more potently binds the MDM2 protein, compared to the PI3K domain. f PLA on AT5 BiVA cells, transfected with different constructs partially lacking domains of ATM, to test the interaction of MDM2 with ATM. g PLA on AT5 BiVA cells, transfected with different phosphomimetic or phospho-impaired ATM constructs at S1981 or S2592. PLA signals show that the ATM-MDM2 interaction is regulated by Ser-2592 and takes place on the FAT and the PI3K domains, whereas the trafficking of the ATM/MDM2 complex to the cytoplasm is regulated by ATM activity and via the phosphorylation of Ser-1981. The asterisks represent P values of three independent experiments, as follows: ‘n/s’ for P > 0.05; ‘*’ for values P ≤ 0.05; ‘**’ for values P ≤ 0.01; and ‘***’ for values P ≤ 0.001. The statistical analyses are based on results obtained by at least 50 cells of each experiment. The cell lines, hybridization probes and antibodies used for each PLA are indicated. h Model describing how the ATM kinase exchanges the p53 mRNA substrate with MDM2, ultimately leading to the phosphorylation of the nascent p53 peptide (p53-Ser-15) that activates p53 towards the DNA damage response