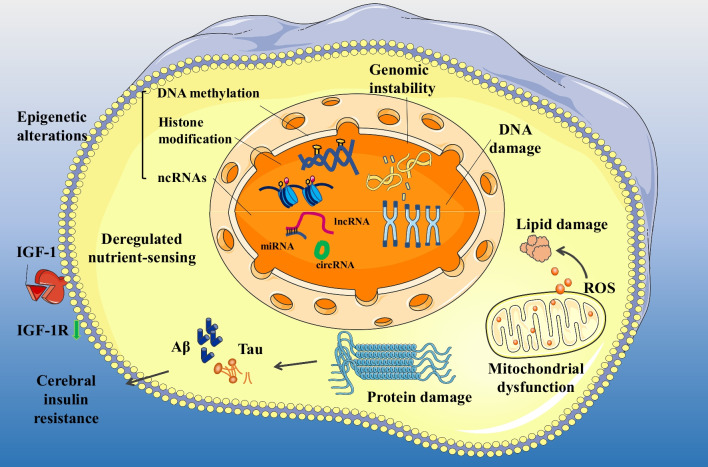
Fig. 1.
Intracellular hallmarks of ageing in AD. The intracellular hallmarks of ageing include genomic instability, macromolecular damage, epigenetic alterations, deregulated nutrient sensing and mitochondrial dysfunction. Additionally, protein damage in AD mainly manifests as the abnormal aggregation of Aβ and tau proteins, which is related to cerebral insulin resistance and affects nutrient sensing in nerve cells [19]. The green arrow indicates that IGF-1R is downregulated in the brain tissues of patients with AD [20]. AD Alzheimer’s disease, ncRNAs non-coding RNAs, lncRNA long non-coding RNA, miRNA microRNA, circRNA circular RNA