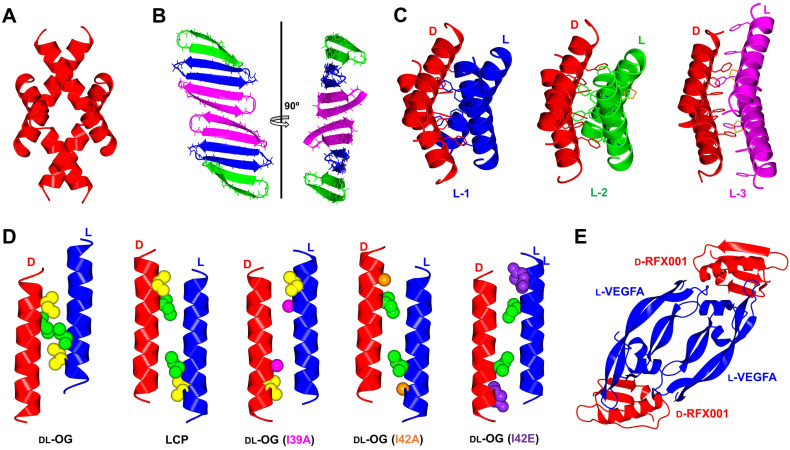
Figure 4.
Quaternary structures by racemic protein crystallography; (A) Melittin tetramer (PDB: 6O4M); (B) BTD‐2 extended fibril‐like structure (PDB: 5INZ); (C) Magainin 2 phenylalanine zipper motif unaffected by β‐amino acid substitutions. D‐magainin 2 is shown in red and mutants L‐1 (Ala) shown in blue (PDB: 4MPG), L‐2 (APC) in green (PDB: 4CGN) and L‐3 (ACPC)(PDB: 5CGO) in magenta. β‐amino acids highlighted in orange; (D) M2‐TM helix forms heterochiral coiled coils, with a hendecad repeat identified in lipidic cubic phase (LCP, PDB: 4RWB) but absent in racemic β‐octylglucoside (DL‐OG, PDB: 4RWC). Mutation of sterically disruptive isoleucine residues to alanine (DL‐OG(I39A), PDB: 6MPL), (DL‐OG(I42A), PDB: 6MPM) or glutamate (DL‐OG(I42E), PDB: 6MPN) favored hendecad repeat motifs in chiral lipids; (E) Quaternary structure of VEGF‐A dimer bound to two D‐protein antagonist molecules (PDB: 4GLN). All structures were modelled in CCP4MG [58] with data obtained from the Protein Data Bank.