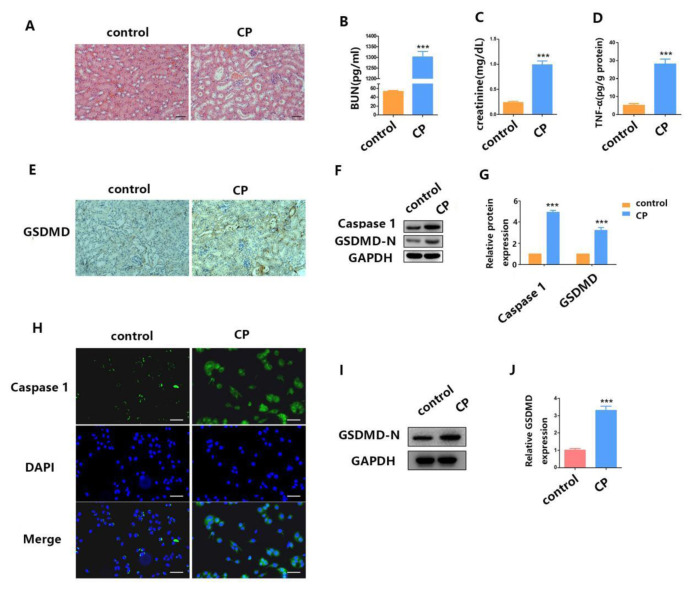
Fig. 1.
Cisplatin induces mouse AKI and RTECs pyroptosis. (A) H&E staining assays were performed 24 h after surgery in both the cisplatin-induced AKI mouse model group and the control group. (B–D) After AKI was induced by cisplatin treatment, we checked the blood for BUN, serum creatinine, and TNF-α concentration. (E) The distribution of GSDMD in kidney tissues as measured by IHC. (F–G) WB analysis of caspase-1 and GSDMD-N expression in cisplatin-induced AKI mice. (H) IF staining shows expression of caspase-1 (green) in cisplatin-treated HK2 cells; Blue fluorescence represents the nucleus (DAPI). Bar, 100 mm. (I–J) WB analysis of caspase-1 and GSDMD-N expression in cisplatin-treated HK2 cells. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences from the control (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).