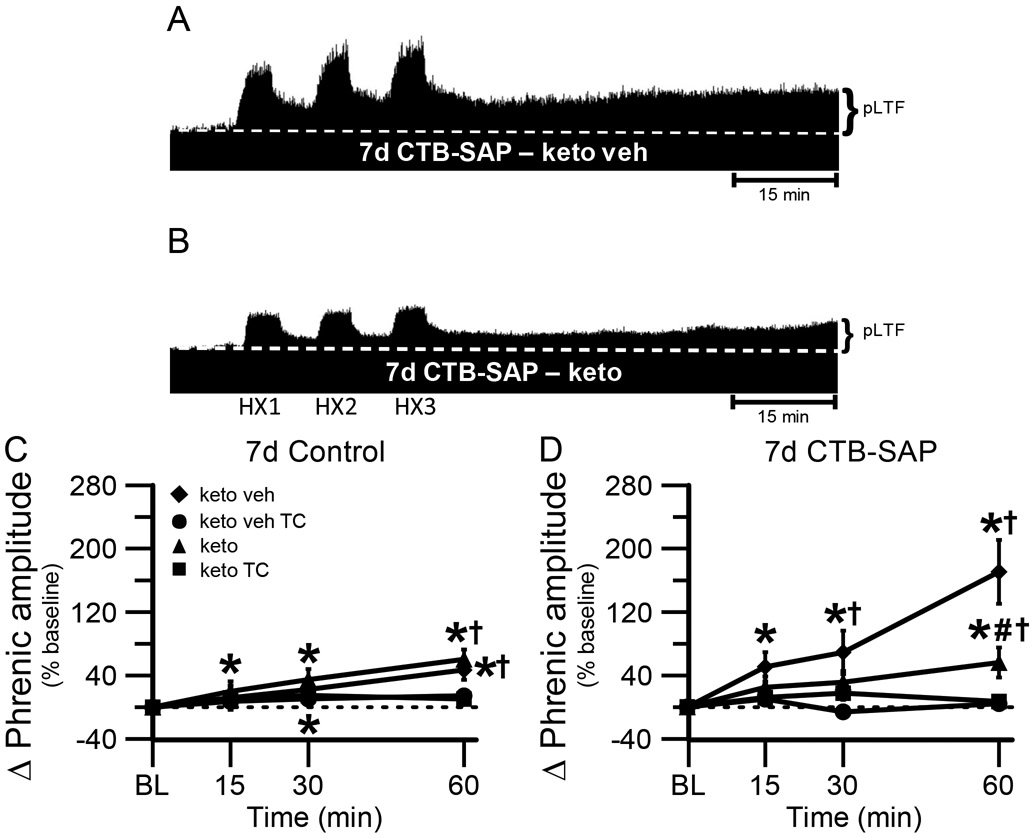
Fig. 2.
pLTF in 7d treated rats. A and B, Representative traces of compressed, integrated phrenic nerve activity before and after AIH in 7d CTB-SAP rats pre-treated with keto veh (A) or keto (B). Baseline is indicated in each trace by a white, dashed line. AIH elicits an enhanced pLTF in 7d CTB-SAP rats pre-treated with keto veh, while pLTF appears to be more moderate with keto pre-treatment. C, D. Phrenic burst amplitude (expressed as a percent change from baseline) in 7d control (C) and 7d CTB-SAP (D) rats pre-treated with keto veh, keto veh TC, keto, or keto TC. pLTF was significantly increased from baseline (*) at all time points in 7d control rats pretreated with keto and at 30 and 60 min post-hypoxia in those pre-treated with keto veh. pLTF was significantly increased from respective TCs at 60 min (†) in 7d control (C) and CTB-SAP (D) rats pre-treated with keto or keto veh. pLTF was significantly increased from baseline (*) at all time points in 7d CTB-SAP rats pre-treated with keto veh and at 60 min for those pre-treated with keto. 7d CTB-SAP rats pre-treated with keto had a pLTF that was significantly less than that of 7d CTB-SAP rats pre-treated with keto veh (#). Values are expressed as means ±1 S.E. M, and differences were considered significant if p < 0.05.