FIGURE 9:
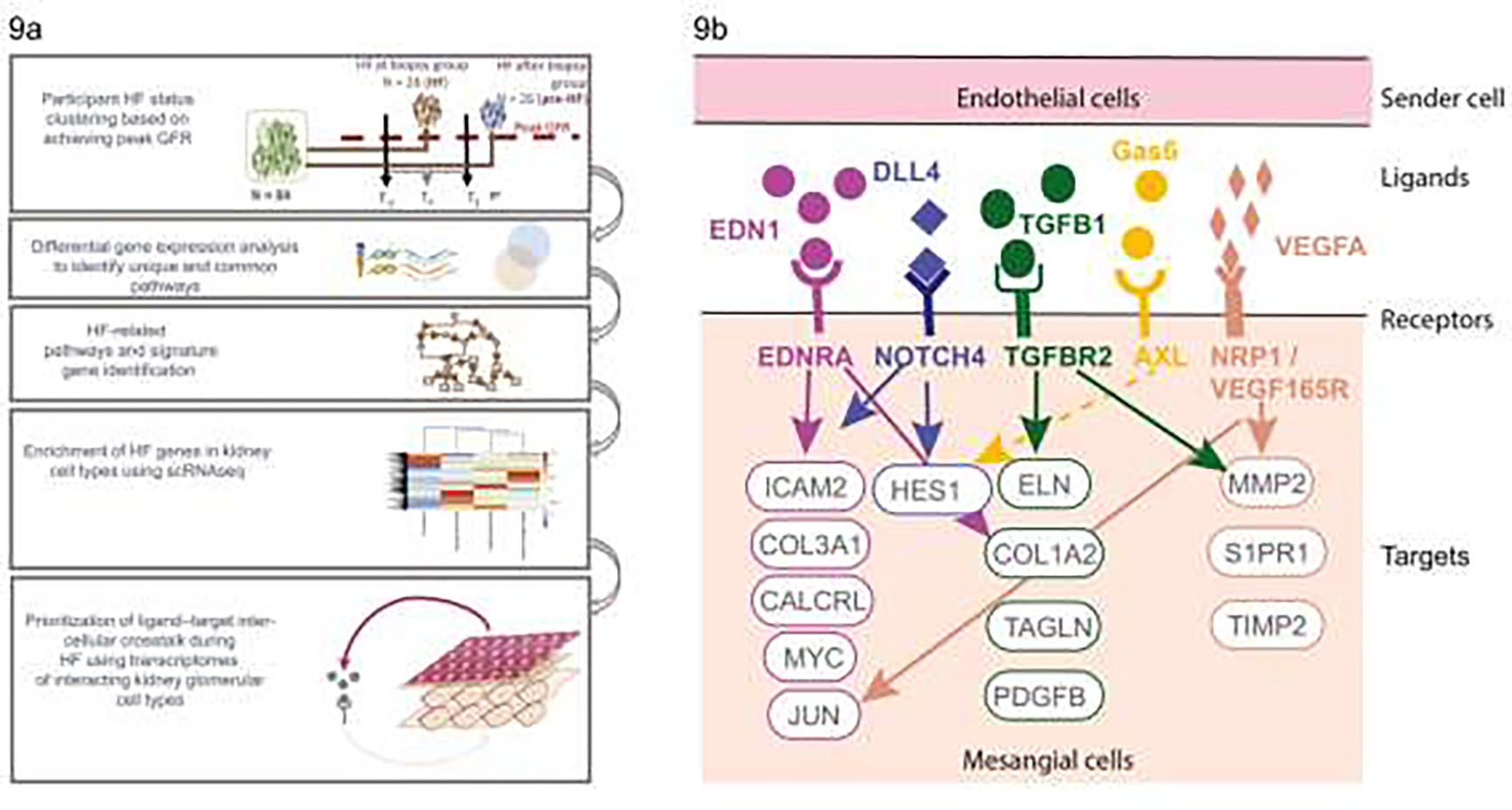
a) Diagram outlining the hyperfiltration study design showing the groups defined based on timing of peak GFR in relation to kidney biopsy, and interrogation of gene expression data to identify genes associated with hyperfiltration followed by examination of single cell data to identify cell types associated with the enriched hyperfiltration genes leading to development of a model for cross-talk between cell types in hyperfiltration (From Steffansson et al, 2022)83; b) molecular insights into hyperfiltration associated with early DKD. CALCRL, calcitonin receptor like receptor; COL1A2, collagen type I alpha 2 chain; COL3A1, collagen type III alpha 1 chain; DLL4, delta-like canonical notch ligand 4; EDN1, endothelin-1; EDNRA, endothelin receptor A; ELN, elastin; Gas6, growth arrest–specific gene 6; HES1, hes family bHLH transcription factor 1; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; JUN, Jun proto-oncogene; MMP2, matrix metallopeptidase 2; MYC, MYC proto-oncogene; NOTCH4, notch receptor 4; NRP1, neuropilin 1; PDGFB, platelet derived growth factor subunit B; S1PR1, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1; TAGLN, transgelin; TGFB1, transforming growth factor-β1; TGFBR2, transforming growth factor-β receptor 2; TIMP2, TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2; VEGF165R, vascular endothelial growth factor 165 receptor; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A (From Steffansson et al, 202283).
