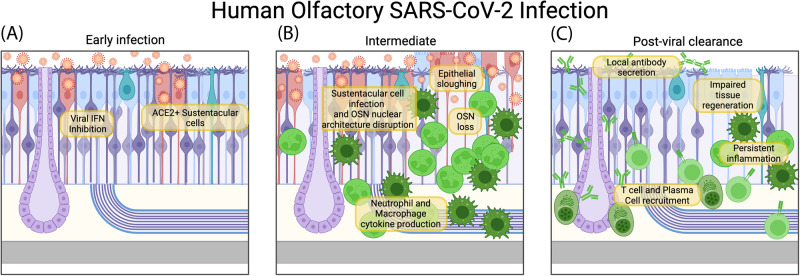
Fig. 1. Olfactory immune response to SARS-CoV-2 in Humans.
The stages of the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 in the olfactory mucosa. A SARS-CoV-2 uses ACE2 to enter sustentacular cells and antagonize the induction of interferons. B Infiltrating neutrophils and macrophages produce inflammatory cytokines. Sustentacular cells are lost, epithelial structure deteriorates, and olfactory sensory neurons undergo disruption of nuclear architecture and cell death. C After SARS-CoV-2 has been cleared by the immune response, T cells and plasma cells populate the tissue. Plasma cells produce locally protective mucosal antibody. T cells may contribute to sustained inflammation, preventing proper epithelial regeneration in some cases and preventing restoration of the sense of smell