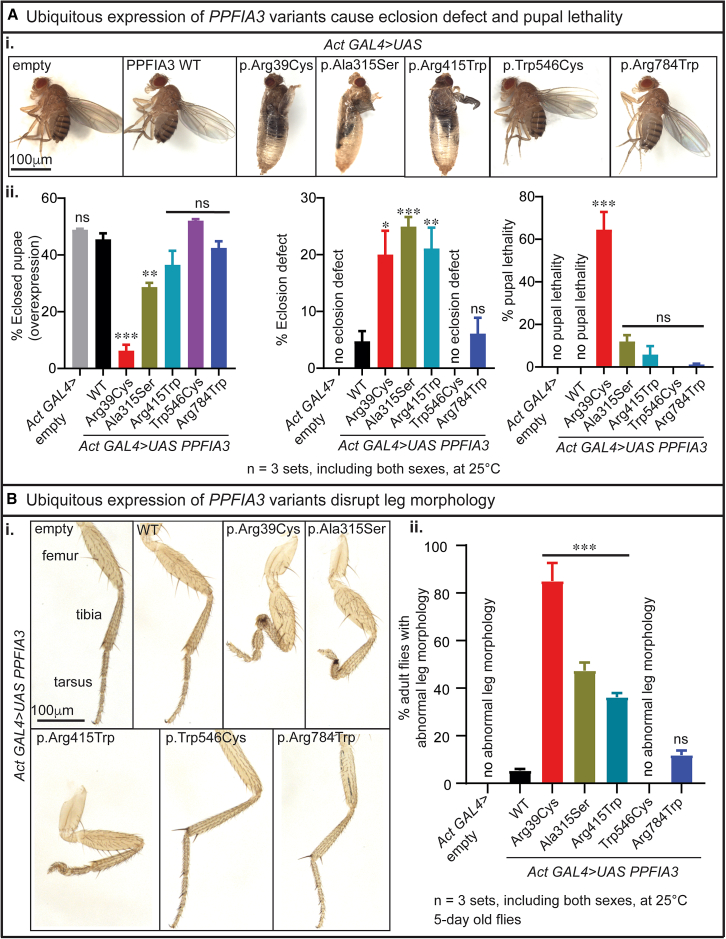
Figure 3.
Actin-GAL4-mediated ubiquitous expression of PPFIA3 variants cause developmental and anatomical defects in fruit flies
(A) Pupal lethality and eclosion defect associated with Actin-GAL4-mediated overexpression of PPFIA3 variants.
(i) Images showing overexpression of PPFIA3 p.Arg39Cys cause pupal lethality and eclosion defect, and p.Ala315Ser and p.Arg415Trp cause eclosion defect compared to the PPFIA3 WT and UAS-empty control. Uneclosed flies from p.Arg39Cys, p.Ala315Ser, and p.Arg415Trp remain in the pupal case. PPFIA3 p.Trp546Cys and p.Arg784Trp overexpression does not cause a difference in pupal lethality and eclosion defect compared to PPFIA3 WT and UAS-empty control flies. Scale bar = 100 μm.
(ii) Bar graphs showing the percentage of eclosed pupae (overexpression), eclosion defect, and pupal lethal. Statistical analysis conducted with one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc analysis. Data shown as mean ± SEM with the sample size of total number of pupae in three sets. Significance shown as ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Non-significance shown as ns.
(B) Images of leg morphology associated with Actin-GAL4-mediated overexpression of PPFIA3 variants.
(i) Empty control and PPFIA3 WT flies have typical legs with three segments. PPFIA3 p.Arg39Cys, p.Ala315Ser, and p.Arg415Trp result in pronounced leg segment developmental defects compared to PPFIA3 WT. Mild leg segmental developmental defects found with PPFIA3 p.Arg784Trp but not significant compared to PPFIA3 WT. No leg defects were found in PPFIA3 p.Trp546Cys flies. Scale bar = 100 μm.
(ii) Bar graph showing the percentage of flies with abnormal leg morphology. Statistical analysis conducted with one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc analysis. Data shown as mean ± SEM with the sample size of total number of adult flies in three sets. Significance shown as ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Non-significance shown as ns.