Figure 5.
PPFIA3 WT partially rescues the fly Liprin-α LOF lethality
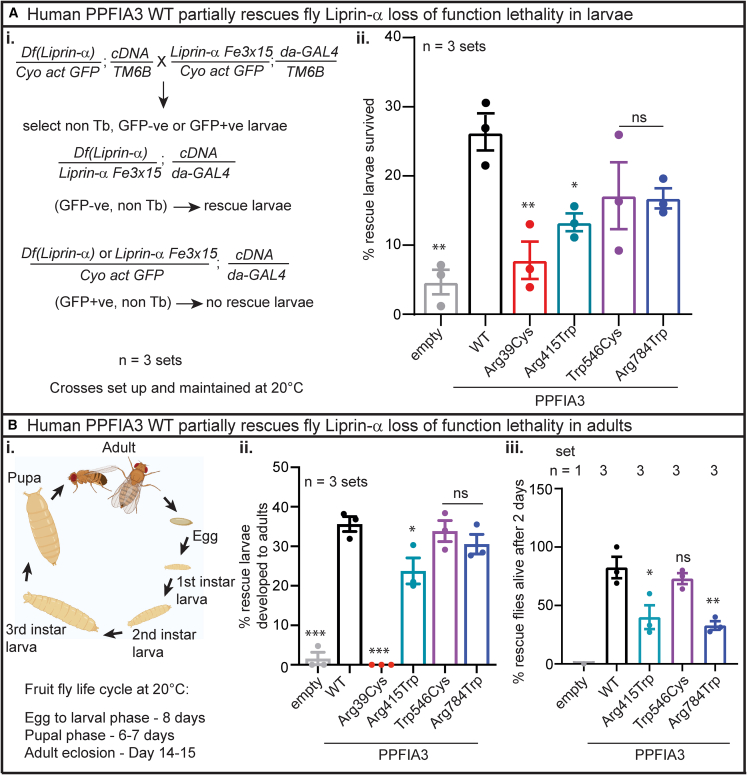
(A) Human PPFIA3 WT in the background of fly Liprin-α LOF results in a partial rescue of embryonic lethality.
(i) Crossing scheme to delete fly Liprin-α and express human PPFIA3 WT and variants. The scheme describes the rescue larvae selection strategy. Crosses were set and maintained at 20°C.
(ii) Quantification of n = 3 sets per genotype showing % GFP-negative larvae (rescue larvae) that survive to the larval stage. PPFIA3 WT expression can partially rescue larval viability compared to empty control. PPFIA3 p.Arg39Cys and p.Arg415Trp show impaired ability to rescue larval viability.
(B) Human PPFIA3 WT expression partially rescues the lethality in adult stage.
(i) Representative illustration of the different stages of fruit fly development.
(ii) Quantification of 3 sets of rescued larvae per genotype that survive to the adult stage. PPFIA3 WT expression can partially rescue adult viability compared to empty control. PPFIA3 p.Arg39Cys and p.Arg415Trp show impaired ability to rescue adult viability.
(iii) Quantification of 1–3 sets of rescued larvae per genotype that survived after 48 h post-eclosion. For the empty control larvae, only one escaper rescue larvae survived to adult stage but died within 2 days post-eclosion. None of the PPFIA3 p.Arg39Cys rescue larvae survived to adult stage. Due to the lack of any PPFIA3 p.Arg39Cys rescue larvae surviving to the adult stage, this variant was not quantifiable for the adult survival phenotype. PPFIA3 p.Arg415Trp and PPFIA3 p.Arg784Trp show impaired ability to rescue adult viability compared to the PPFIA3 WT. Sample size is shown in Table S2. Statistical analysis with one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc analysis. Data shown as mean ± SEM with the sample size of flies scored shown in (Table S2). Significance shown as ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Non-significance shown as ns.