Abstract
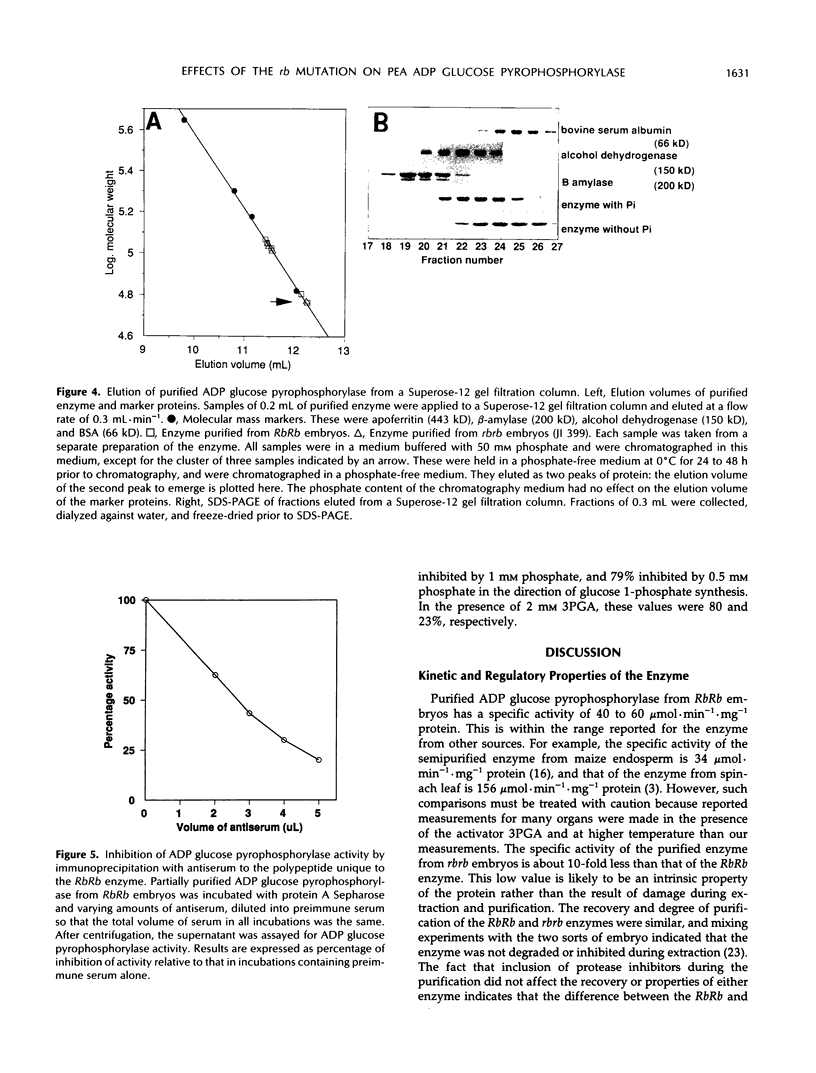
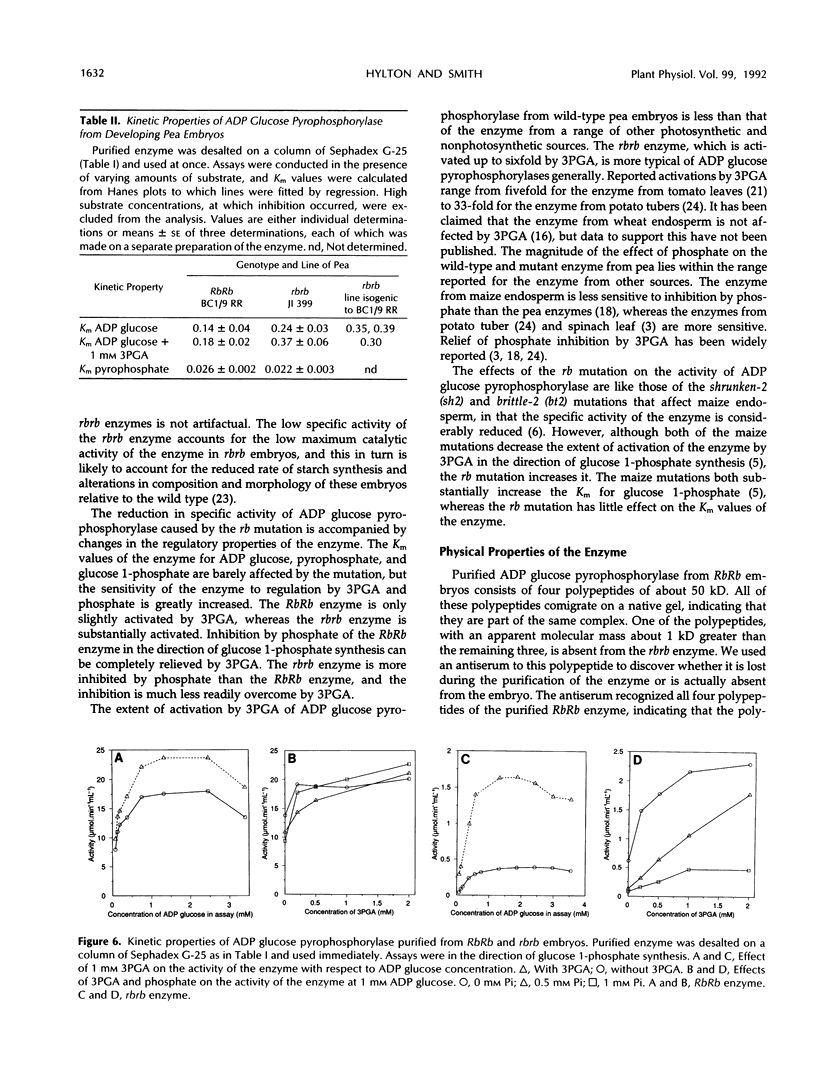
A mutation at the rb locus of pea (Pisum sativum L.) alters the shape, reduces the starch content, and increases the lipid and sucrose contents of the seed. These effects are probably all consequences of a reduction of up to 40-fold in the maximum catalytic activity of ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase in the developing embryo of the mutant relative to the wild type. We have investigated how the mutation brings about this reduction in activity. The purified enzyme from mutant embryos has a specific activity about 10-fold lower than that from wild-type embryos, and it is much more sensitive to the effectors inorganic phosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate than the wild-type enzyme. Both wild-type and mutant enzymes consist of polypeptides of around 50 kilodaltons. One of the polypeptides of the purified wild-type enzyme is missing from the mutant enzyme. We deduce that in the wild-type embryo this protein may interact with other subunits to confer a high specific activity and a low susceptibility to effectors on the enzyme.
Full text
PDF


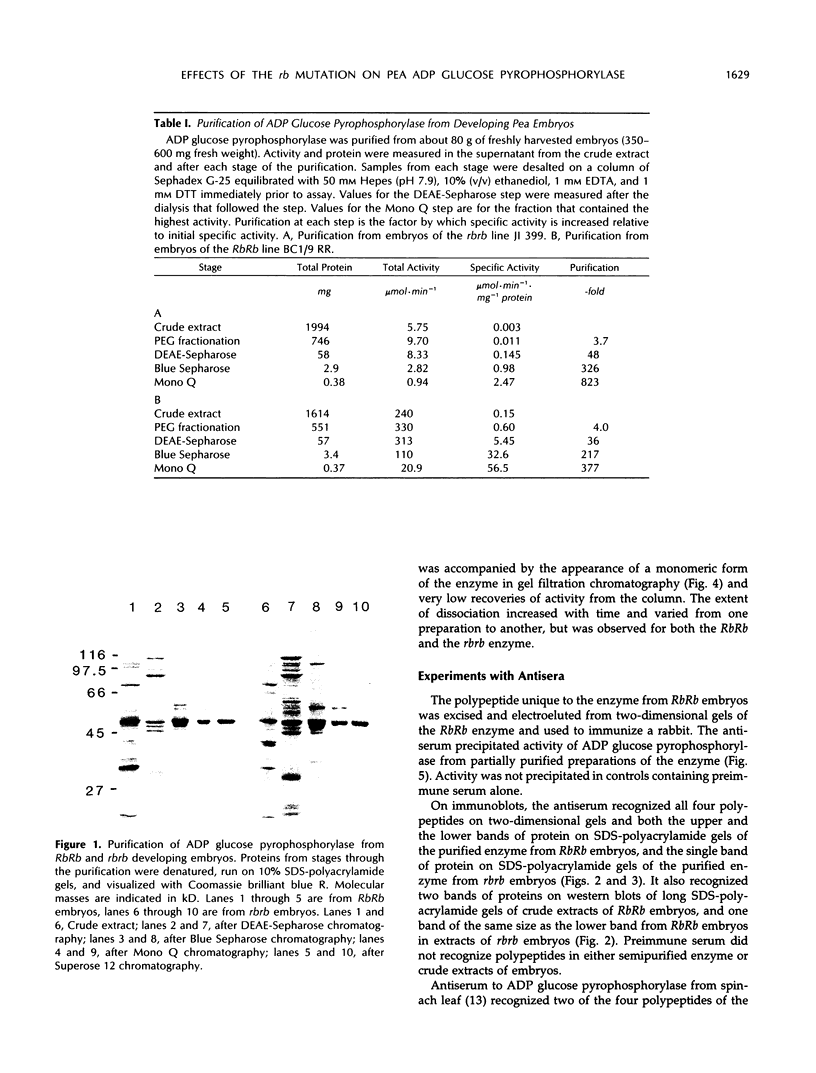



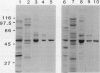
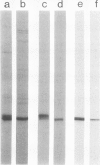
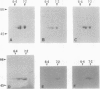
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya M. K., Smith A. M., Ellis T. H., Hedley C., Martin C. The wrinkled-seed character of pea described by Mendel is caused by a transposon-like insertion in a gene encoding starch-branching enzyme. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90721-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland L., Preiss J. Purification of Spinach Leaf ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):996–1001. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. B., Preiss J. Presence of ADP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase in Shrunken-2 and Brittle-2 Mutants of Maize Endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jul;44(7):1058–1062. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.7.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannah L. C., Nelson O. E. Characterization of adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylases from developing maize seeds. Plant Physiol. 1975 Feb;55(2):297–302. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan H. B., Reeves C. D., Okita T. W. ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase Is Encoded by Different mRNA Transcripts in Leaf and Endosperm of Cereals. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):642–645. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. P., Caspar T., Somerville C. R., Preiss J. A Starch Deficient Mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana with Low ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase Activity Lacks One of the Two Subunits of the Enzyme. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1175–1181. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. P., Caspar T., Somerville C., Preiss J. Isolation and Characterization of a Starchless Mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh Lacking ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase Activity. Plant Physiol. 1988 Apr;86(4):1131–1135. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.4.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell M. K., Bloom M., Knowles V., Preiss J. Subunit Structure of Spinach Leaf ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):182–187. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell M., Bloom M., Preiss J. Affinity labeling of the allosteric activator site(s) of spinach leaf ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Nakata P. A., Anderson J. M., Sowokinos J., Morell M., Preiss J. The Subunit Structure of Potato Tuber ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jun;93(2):785–790. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.2.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaxton W. C., Preiss J. Purification and Properties of Nonproteolytic Degraded ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase from Maize Endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jan;83(1):105–112. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Danner S., Summers P. S., Morell M., Barton C. R., Yang L., Nieder M. Molecular Characterization of the Brittle-2 Gene Effect on Maize Endosperm ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase Subunits. Plant Physiol. 1990 Apr;92(4):881–885. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.4.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal G. G., Greenberg E., Hardie J., Cameron E. C., Preiss J. Regulation of starch biosynthesis in plant leaves: activation and inhibition of ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol. 1968 Mar;43(3):417–427. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. M., Bettey M., Bedford I. D. Evidence that the rb Locus Alters the Starch Content of Developing Pea Embryos through an Effect on ADP Glucose Pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol. 1989 Apr;89(4):1279–1284. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.4.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowokinos J. R., Preiss J. Pyrophosphorylases in Solanum tuberosum: III. PURIFICATION, PHYSICAL, AND CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF ADPGLUCOSE PYROPHOSPHORYLASE IN POTATOES. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jun;69(6):1459–1466. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.6.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]