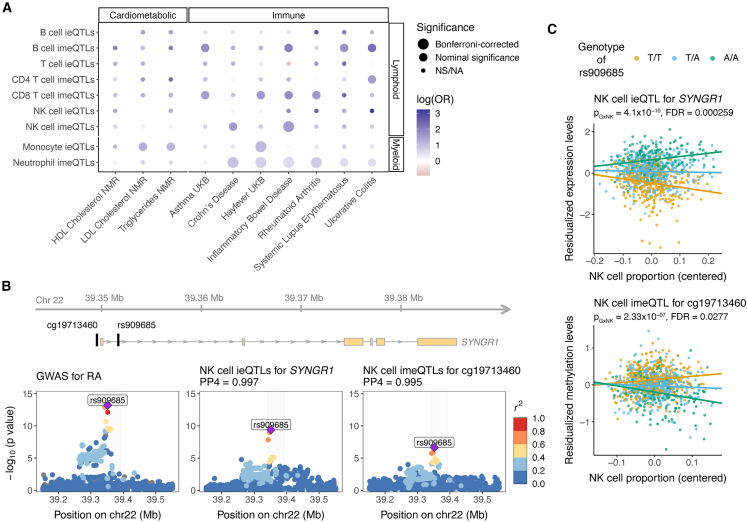
Figure 5.
Cell-type interaction QTLs and relevance for diseases
(A) Relevance of cell-type ieQTLs (FDR < 0.25) and cell-type imeQTLs (FDR < 0.05) for selected cardiometabolic and immune diseases compared to height. For each of the cell-type iQTLs, we calculated the odds ratio (OR) as the ratio of the odds that an iQTL would colocalize with a cardiometabolic or immune disease to the odds that an iQTL would colocalize with height. For testing the significance of the OR, at least 10 loci had to be tested for colocalization; otherwise, the significance is noted as NA (not available). Bonferroni correction was applied separately for cell-type ieQTLs and cell-type imeQTLs. NS: not significant.
(B) Colocalization between GWAS for RA by Okada et al.,36 NK-cell ieQTLs for SYNGR1, and imeQTLs for a nearby CpG site cg19713460, shown as regional association plots. The highlighted region is depicted at the top and shows the location of rs909685, the lead GWAS variant for RA, and the CpG site relative to SYNGR1.
(C) Association plot for the NK cell ieQTL for SYNGR1 and the NK-cell imeQTL for cg19713460. The p value of the interaction effect from the linear model fitted with TensorQTL is shown. Dots are colored on the basis of the genotype of rs909685. Data in (B) and (C) are from exam 1, where we observed the lowest interaction p values.