Fig. 4. Endoplasmic Reticulum Associated Degradation and Proteotoxic Stress.
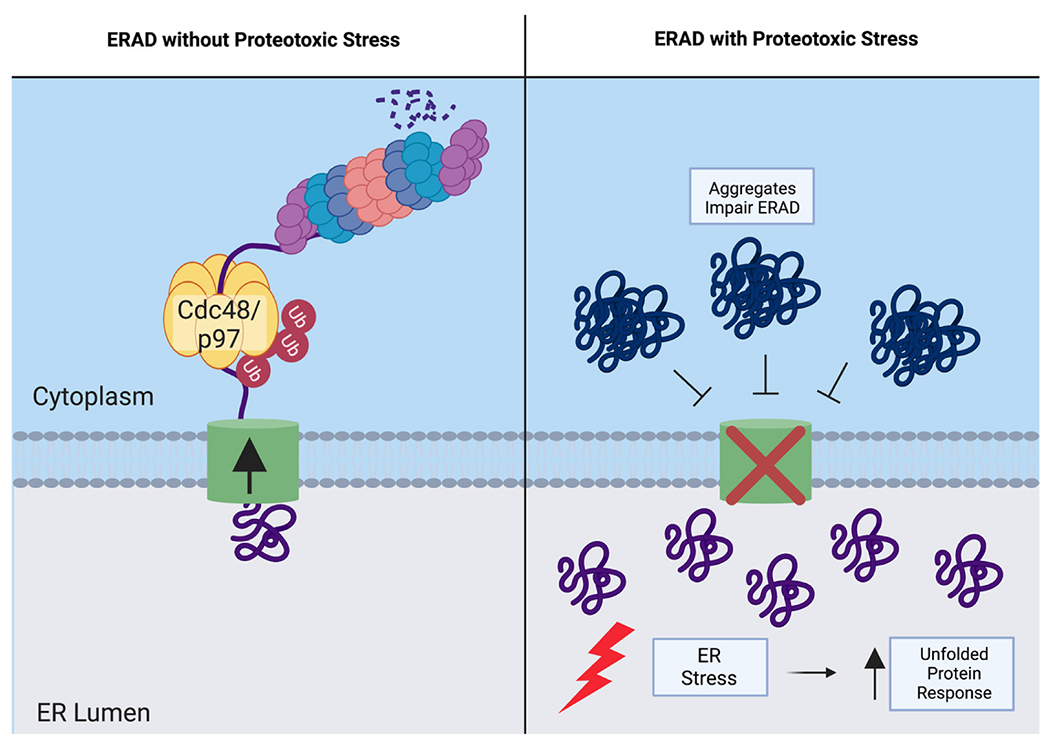
The left panel of the figure depicts the role of ERAD under normal physiological conditions. Misfolded proteins are retrotranslocated from the ER lumen into the cytoplasm, in a ubiquitin-dependent process that requires a retro-translocon and the ATPase p97/VCP in mammalian cells and Cdc48 in yeast cells. The right panel depicts that proteotoxic stress from protein aggregates can lead to impairment of ERAD. This impairment increases proteotoxic stress specifically at the ER and leads to activation of the UPR, a pathway that aims to restore ER proteostasis. Created with BioRender.com.
