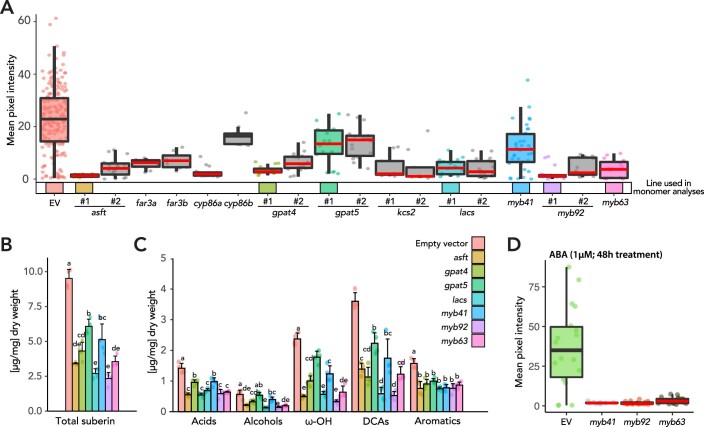
Extended Data Fig. 6. R. rhizogenes-derived loss-of-function mutant alleles of candidate genes have impaired suberin deposition.
(a) Extended analysis of mutant phenotypes of candidate genes in hairy roots (HR). Mean fluorol yellow signal across multiple cross sections (wild type n = 66; rest n = 6). Red line indicates statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) in fluorol yellow pixel intensity in the mutant vs wild type as determined with a one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey-Kramer post hoc test. In most cases, two independently generated HR lines were analyzed, as indicated in the plot. (b) Mean suberin abundance and (c) monomer composition of R. rhizogenes-generated mutants of suberin biosynthetic enzymes and transcriptional regulators. Acid: fatty acids; Alcohols: primary alcohols; ω-OH: ω-hydroxy fatty acids; DCA: dicarboxylic fatty acid; Aromatics: ferulate and coumarate derivatives. Error bars: SD. Letters indicate significant differences (one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey-Kramer post hoc test, P < 0.05). (d) ABA treatment (1 µM for 48 h) does not restore suberin to wild type levels by fluorol yellow staining in slmyb41, slmyb92 and slmyb63 lines. Mean pixel intensities are not comparable between plots A and D as these were taken under different laser settings.