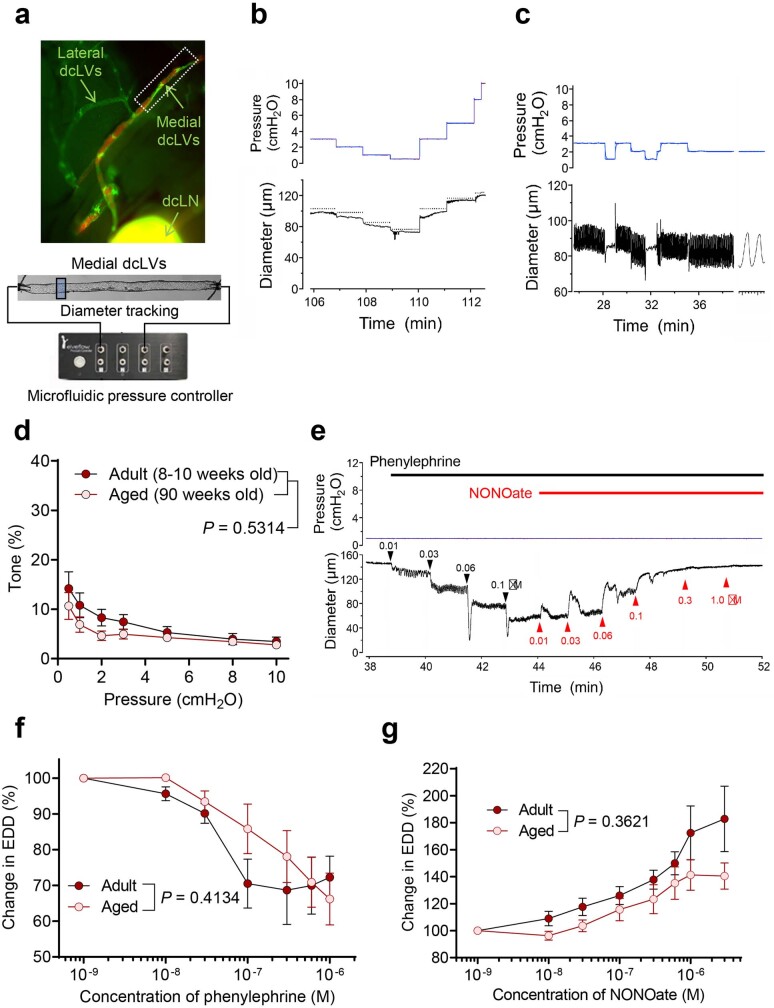
Extended Data Fig. 12. Active responses of ex vivo medial deep cervical lymphatics to pressure, phenylephrine, and NONOate.
a, Images showing medial deep cervical lymphatics (medial dcLVs) in situ and after cannulation ex vivo for measuring diameter and intraluminal pressure. The experimental setup enabled diameter measurements of isolated, cannulated lymphatics with intraluminal pressure governed by a microfluidic pressure controller. White box marks the segment of medial dcLVs typically dissected for ex vivo studies. b, Response of typical medial dcLV to pressure steps over the physiological range 0.5 to 10 cmH2O. Only small spontaneous amplitude fluctuations are evident at lower pressures. Dotted lines indicate the passive diameter at each pressure, as determined in Ca2+-free Krebs at the end of the experiment. c, Example of medial dcLV with large-amplitude spontaneous diameter changes (contractions) at pressure settings of 1 or 2 cmH2O. Diameter changes ceased at 0.5 cmH2O. Contraction frequency was 13-14 per min. Expanded trace on far right shows two individual contractions, each with a duration of 2.4 sec. d, Plot of active tone as a function of intraluminal pressure in medial dcLVs from adult (8-10 weeks old; n = 10) and aged (90 weeks old; n = 12) mice. Tone was calculated as the difference in active and passive end-diastolic diameter at each pressure and expressed as a percentage of the passive diameter at that pressure. Bars present mean ± s.e.m. P value was calculated by two-way repeated measures ANOVA. e, Recordings of pressure and diameter that illustrate the dosing protocol for inducing tone and assessing concentration-dependent responses to phenylephrine, followed by assessment of concentration-dependent responses to sodium NONOate, at a constant pressure of 1 cmH2O. Small spontaneous contractions follow the first exposure to phenylephrine (10 nM). f, Lack of age-related difference in concentration-dependent constrictions to phenylephrine in medial dcLVs from adult (8-10 weeks old; n = 11) and aged (90 weeks old; n = 12) mice. EDD, end diastolic diameter. Bars present mean ± s.e.m. P value was calculated by a mixed effect analysis. g, Lack of age-related difference in concentration-dependent dilatations to sodium NONOate (in the continued presence of phenylephrine) in adult (8-10 weeks old; n = 11) and aged (90 weeks old; n = 12) mice. EDD, end diastolic diameter. Bars present mean ± s.e.m. P value was calculated by two-way repeated measures ANOVA.