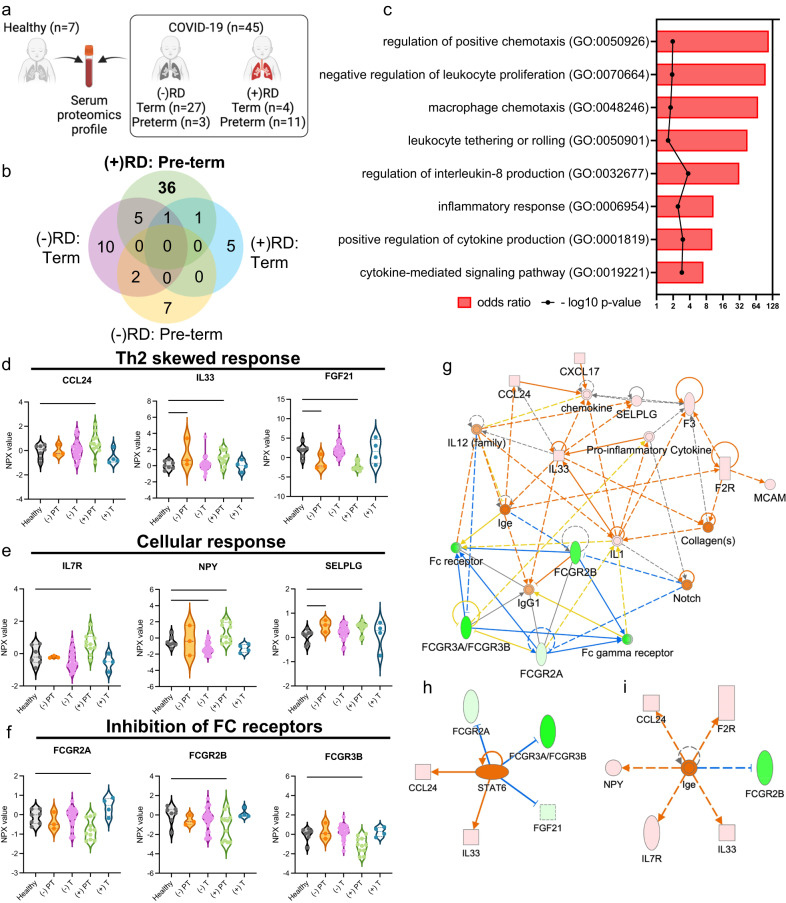
Fig. 4. Proteomic analysis in a subset of SARS-CoV-2 exposed uninfected infants (n = 45) compared to control infants born to healthy mothers (n = 7).
a. Schematic representation of serum proteome multiplexing of COVID-19-affected (COVID-19) infants. Infant blood specimens were collected from infants within the first 2 days of life born to healthy mothers (n = 7) or to SARS-CoV-2-infected mothers (n = 45). COVID-19-exposed infants were clustered according to pregnancy duration and the absence (-) (preterm n = 3, and term n = 27) or presence (+) (preterm n = 11, and term n = 4) of respiratory distress (RD). Created with BioRender.com. b Quantitative comparison of cytokines significantly altered (p < 0.05; −2 < FC > 2) in COVID-19 infants with or without respiratory distress, (−) or (+) RD, respectively, in contrast to cytokines observed in pre-term and term pregnancy in both groups. Quantitative analysis in all groups relative to healthy controls, p values were determined based on two-tailed Mann Whitney U Test considering fold-change ≥2 and FDR-adjusted p-value < 0.05. c. Enricher, Gene ontology biological pathways upregulated exclusive for COVID-19-exposed infants (+) RD pre-term compared with healthy controls; p values obtained from a one-way ANOVA with uncorrected Fisher’s test. Proteins upregulated and downregulated in infants from COVID-19 pregnancy (+) RD pre-term, related with (d) Th2 skewed response, (e) activation of cellular response and (f) inhibition of FC receptors. Data are presented as means ± SEMs, using 1-way one-way ANOVA with uncorrected Fisher’s test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, ****p < 0.001; please see text for exact p values. g IPA predicted functional networks exclusive for COVID-19 pregnancy (+) RD pre-term compared with healthy controls. h Proteins differentially expressed (PDEs) associated with Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 6 (STAT6) pathways among SARS-CoV-2 exposed uninfected preterm neonates. i PDEs associated with higher IgE production among SARS-CoV-2 exposed uninfected preterm neonates.