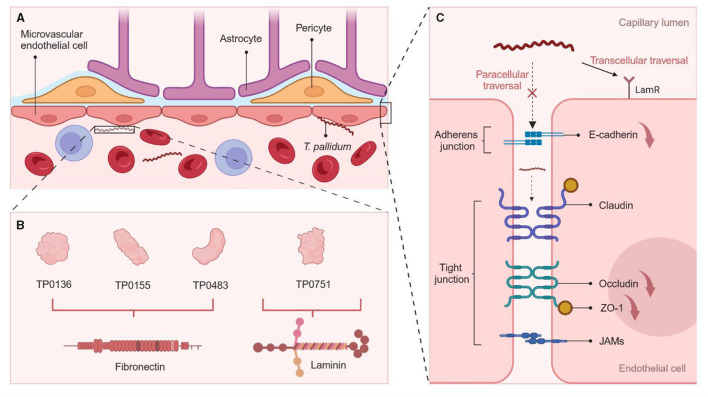
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of T. pallidum for Crossing the BBB. (A) The BBB is composed of brain microvascular endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes. Attaching to the host cells is the first step in T. pallidum neuroinvasion (33). (B) Several T. pallidum proteins are identified to be adhesins, including laminin- (TP0751) and fibronectin- (TP0136, TP0155, TP0483) binding proteins (34). (C) T. pallidum adheres to endothelial cells at the site of intercellular junction, resulting in a notable reduction in the expression of tight junction proteins ZO-1 and occludin through TP0751, and disrupting VE-cadherin, thereby entering the BBB through a paracellular pathway; TP0751 coordinates intercellular transport by engaging with host receptors (LamR) in lipid rafts and inducing endothelial uptake and transport in a cholesterol-dependent manner (35). The figure was created in BioRender.