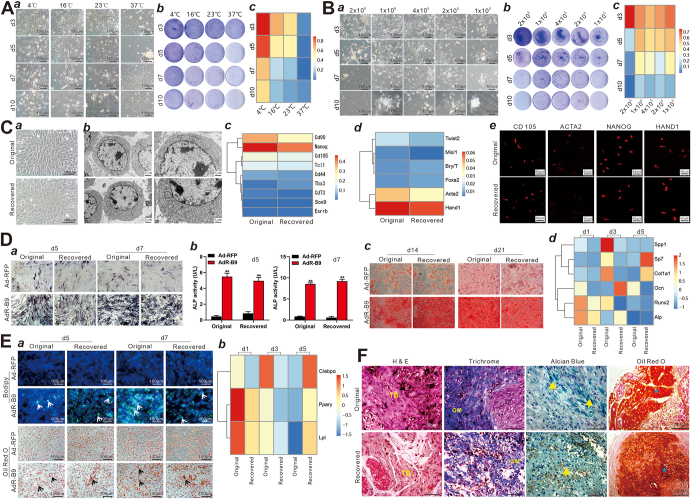
Figure 1.
A simplified noncryogenic strategy to transport mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). (A) The effect of storage/transport temperatures on the survival of iMEFs. 2 × 105 iMEFs were suspended in 1 mL of 10% FBS DMEM in 1.5 mL sterile Eppendorf tubes, and kept at 4 °C, 16 °C, 23 °C, and 37 °C, separately, for 3, 5, 7, and 10 days. (a) The recovered iMEFs were plated and observed at 24 h under a bright field microscope (×200). (b) Crystal violet cell viability assay. The recovered iMEFs were plated in 35 mm cell culture dishes and stained with crystal violet at 24 h. Representative images are shown. (c) Flow cytometry-based apoptosis analysis. The original and recovered iMEFs were plated in 35 mm cell culture dishes, collected at 24 h, and stained with annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide (PI) for flow cytometry. More detailed flow cytometry results are presented in Figure S1. (B) The effect of cell densities on the survival of iMEFs. The iMEFs at 2 × 106/mL, 1 × 106/mL, 4 × 105/mL, 2 × 105/mL, and 1 × 105/mL were separately suspended in 1 mL of 10% FBS DMEM in 1.5 mL sterile Eppendorf tubes and kept at 16 °C for 3, 5, 7, and 10 days. (a) Macrographic images of the recovered iMEFs. The recovered iMEFs were plated in 35 mm cell culture dishes and observed at 24 h under a bright field microscope (×200). Representative images are shown. (b) Crystal violet cell viability assay. The recovered iMEFs were plated in 35 mm cell culture dishes and stained with crystal violet at 24 h. Representative images are shown. (c) Flow cytometry-based apoptosis analysis. The original and recovered iMEFs were plated in 35 mm cell culture dishes, collected at 24 h, and stained with annexin V-FITC and PI for flow cytometry. More detailed flow cytometry results are presented in Figure S2. (C) The cell morphology and characteristics of marker gene expression of the recovered iMEFs. 4 × 105 iMEFs were suspended in 1 mL of 2% FBS DMEM in 1.5 mL sterile Eppendorf tubes at 16 °C for 10 days. The original and recovered iMEFs were separately plated in 35 mm cell culture dishes and observed under a bright field microscope at 24 h (×100, ×200) (a) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) (×8000, ×15000) (b). (c,d) TqPCR analysis. The original and recovered iMEFs were separately plated in 100 mm cell culture dishes and collected for RNA isolation at 24 h. TqPCR analysis was carried out to detect the expression of stemness markers (c) and mesoderm markers (d). More detailed results are presented in Figure S6. (e) Immunofluorescence (IF) staining of MSC markers. The original and recovered iMEFs were separately seeded in chamber slides for 24 h and subsequently subjected to IF staining with antibodies against CD105, NANOG, ACTA2, and HAND1. The nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI (×400). Representative images are shown. More detailed results and negative controls are presented in Figure S7. (D) The osteogenic differentiation ability of the recovered iMEFs in vitro. 4 × 105 iMEFs were suspended in 1 mL of 2% FBS DMEM in 1.5 mL sterile Eppendorf tubes and kept at 16 °C for 10 days. The original and recovered iMEFs were separately seeded in 24-well cell plates and infected with AdR-B9 or Ad-RFP for the following assays. Qualitative ALP staining (a) and quantitative ALP activity assay (b) were carried out on days 5 and 7. Representative images are shown in (a). ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗P < 0.05, original iMEFs vs. the recovered iMEFs at the indicated time points. (c) Alizarin red staining was done on days 14 and 21. Representative images are shown. (d) TqPCR analysis was carried out to detect the expression of osteogenic markers on days 1, 3, and 5. Detailed results are shown in Figure S8. (E) The adipogenic differentiation ability of the recovered iMEFs in vitro. 4 × 105 iMEFs were suspended in 1 mL of 2% FBS DMEM in 1.5 mL sterile Eppendorf tubes and kept at 16 °C for 10 days. The original and the recovered iMEFs were separately seeded in 24-well cell plates and infected with AdR-B9 or Ad-RFP. (a) Bodipy staining (top two rows) and oil red O staining (bottom two rows) were carried out on days 5 and 7. The lipid droplets were indicated by arrows. Representative images are shown. (b) TqPCR analysis was carried out to detect the expression of adipogenic markers on days 1, 3, and 5. Detailed results are shown in Figure S9. (F) The osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation potential of the recovered iMEFs in vivo. The original and recovered iMEFs were separately plated in 100 mm cell culture dishes and infected with AdR-B9 or Ad-RFP for 36 h. The infected cells were collected and subcutaneously injected into the flanks of athymic nude mice. Subcutaneous masses were retrieved from AdR-B9 transduced cell groups after 5 weeks while no masses were retrieved in the Ad-RFP infected cell groups. The retrieved masses were subjected to hematoxylin–eosin staining, Masson's trichrome staining, alcian blue staining, and oil red O staining. Representative images are shown. TB, trabecular bone; OM, osteoid matrix. The cartilage was indicated by yellow arrows. The lipid droplets were indicated by asterisks.