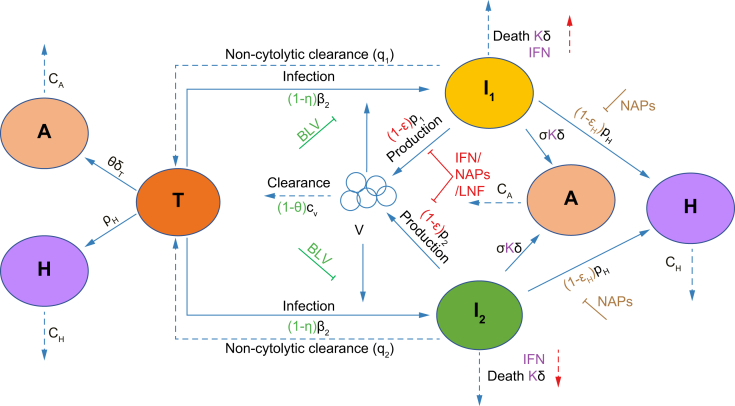
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the model.
Our mathematical model (Eq. 1) incorporates the viral dynamics of HBV-positive HDV-naïve target cells (T), two types of HDV-infected cells (I1 and I2), HDV virions (V), ALT (A), and HBsAg (H). Target cells become infected and convert to I1 at rate β1 and to I2 at rate β2. Virions are cleared at rate cV. I1 and I2 under non-cytolytic clearance to become target cells at rates q1 and q2, and die at rate δ. Infected cells produce virions at rate p. Target cells are produced at rate pT and die at rate δT. ALT is produced by target cell death at rate φ and by infected cell death at rate σ. ALT is cleared from blood at rate cA. HBsAg is produced by target cells and HDV-infected cells at rate pH and cleared from blood at rate cH. BLV blocks infection with efficacy η and may reduce viral clearance with efficacy θ as shown with the green symbols. Blocking of HDV production by IFN, LNF or NAPs is shown using red symbols (parameter ε). Secondary effects of IFN in increasing cell death are reflected by κ >1 and NAPs efficacy in blocking HBsAg production is shown with parameter εH. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BLV, bulevirtide; HBsAg, hepatitis surface antigen; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HDV, hepatitis D virus; IFN, interferon-α/λ; LNF, lonafarnib; NAPs, nucleic acid polymers.