Fig. 10.
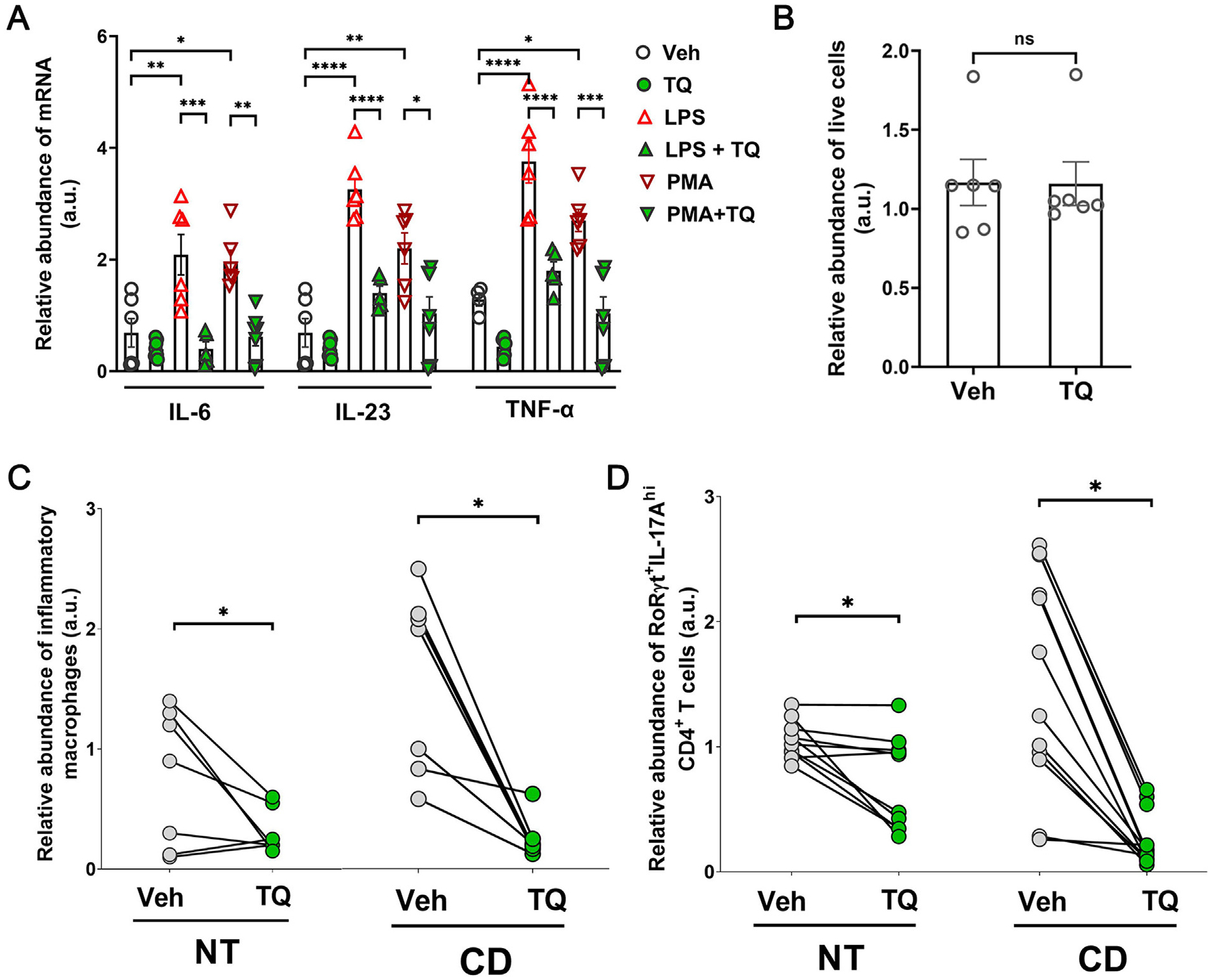
TQ effectively reduces inflammation in human tissues. (A) TQ effectively reduced the upregulation of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α mRNA in human PBMCs when activated with LPS or a cocktail of PMA + ionomycin (PMA). (B) TQ did not affect the cell viability of human PBMCs. (C) In human Crohn’s disease (CD) patient-derived inflamed colonic tissues, TQ treatment reduced the abundance of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β -enriched inflammatory macrophages. Flow cytometry quantification data are represented as the ratio of the absolute number of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β -enriched inflammatory macrophages to the total number of macrophages, pairwise normalized to the average values of three technical replicates for each patient vehicle-treated NT. (D) In human Crohn’s disease (CD) patient-derived inflamed and adjoining normal colonic tissues (NT), TQ treatment reduced the abundance of IL-17A-enriched RORγt+ CD4+ T cells. The flow cytometry quantification data are represented as the ratio of the absolute number of IL-17A-enriched CD4+ T cells to the total number of CD4+ T cells, pairwise normalized to the average values of three technical replicates for each patient vehicle-treated NT. Data represented as mean ± SEM, n ≥ 5/ treatment group. Paired Student’s t-test or one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s post test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. ns = not significant.
