Figure 6. Proposed role of the noncanonical signaling pathways affecting the β-cell secretory function during IGT and T2D.
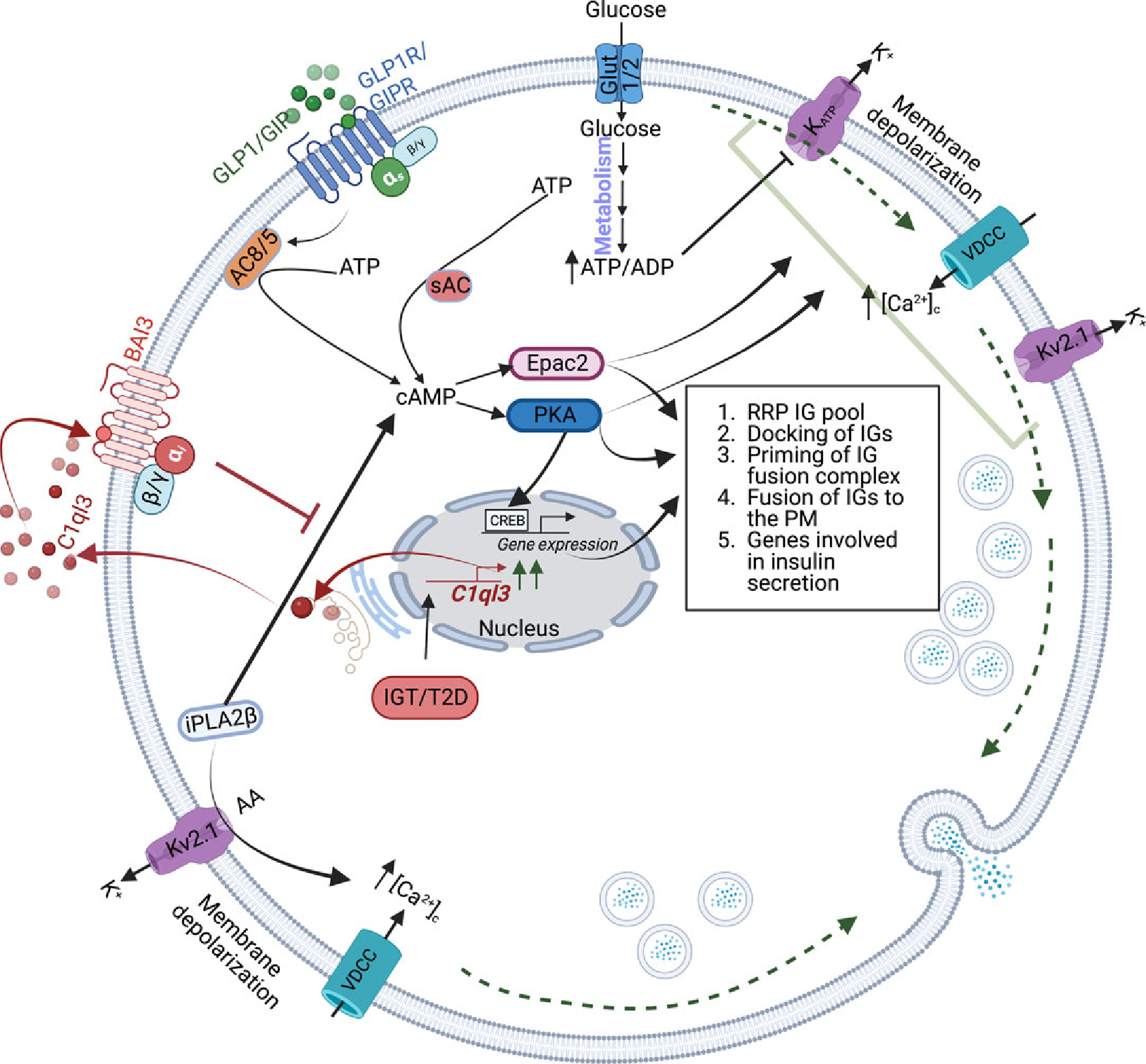
During IGT/T2D, mRNA abundance and the secretion of C1ql3 are increased from the β-cells. The C1ql3 binds to and activates its receptor BAI3 to decrease cAMP signaling, affecting the RRP of IGs, docking of IGs, the priming of IGs, fusion of IGs, and PKA-CREB-regulated expression of genes. Another signaling event mediated by iPLA2β causes an increase in cSIS. The interplay between C1ql3 and iPLA2β in IGT/TD could be important in modulating cAMP signaling, affecting insulin secretion from β-cells during IGT/T2D.
