Fig. 3. Qualitative comparison of landmark localization performance over different annotation conditions.
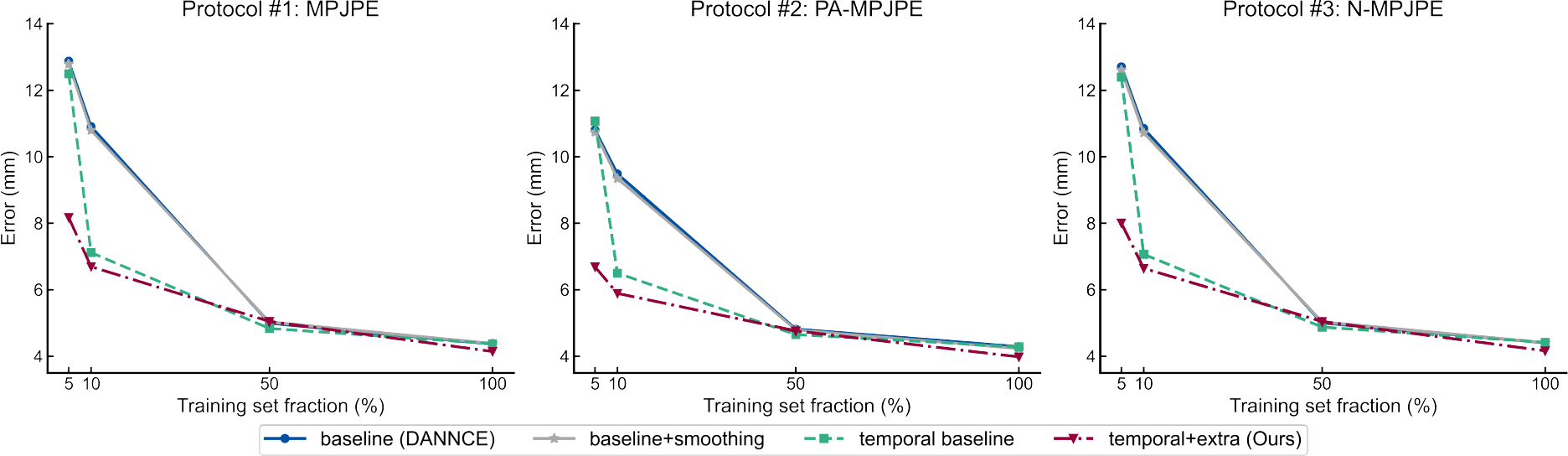
We randomly selected 5% (n = 8), 10% (n=17) and 50% (n=85) of the training set to simulate low annotation regimes. Temporal supervision generally improved performance on all three localization protocols compared to the baseline models, especially with limited access to the training data. Similar improvement cannot be achieved via post hoc smoothing of the predicted movement trajectories.
