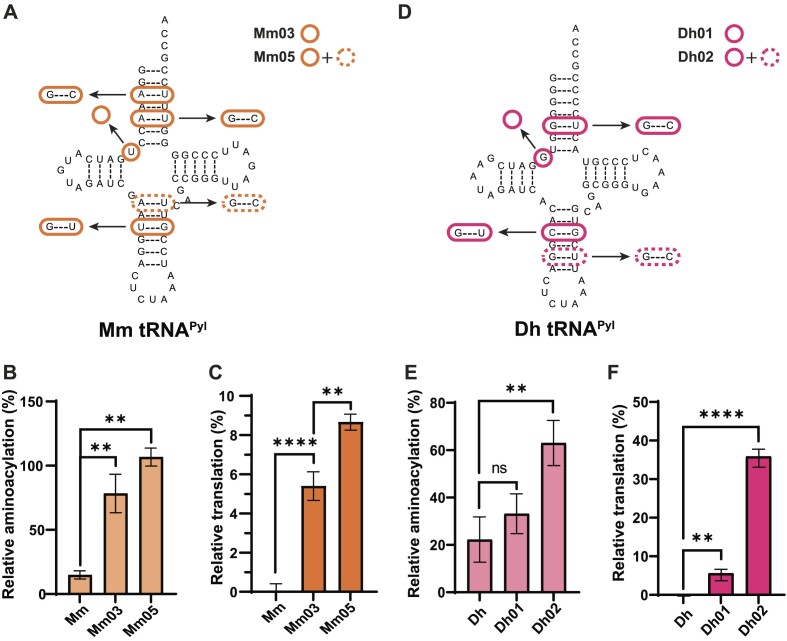
Figure 3.
Transfer of identity elements into other tRNAPyl sequences promotes MaPylRS recognition. (A) Mm tRNAPyl variant cloverleaf structures. Bases that are changed or missing are represented with an orange circle. (B) In vitro assays with Mm tRNAPyl variants show the effect of tRNA mutations on aminoacylation efficiency with MaPylRS. (C) In vivo fluorescent readthrough assays with Mm tRNAPyl variants show the effect of tRNA mutations on translation with MaPylRS. (D) Dh tRNAPyl variant cloverleaf structures. Bases that are changed or missing are represented with a pink circle. (E) In vitro assays with Dh tRNAPyl variants show the effect of tRNA mutations on aminoacylation efficiency with MaPylRS. (F) In vivo fluorescent readthrough assays with Dh tRNAPyl variants show the effect of tRNA mutations on translation with MaPylRS. Data shown is the average of at least three biological replicates with the error bars representing the standard deviation. Percent activity is calculated with Ma tRNAPyl at 100%. Statistical analysis performed with a paired t-test and significance represented as stars.