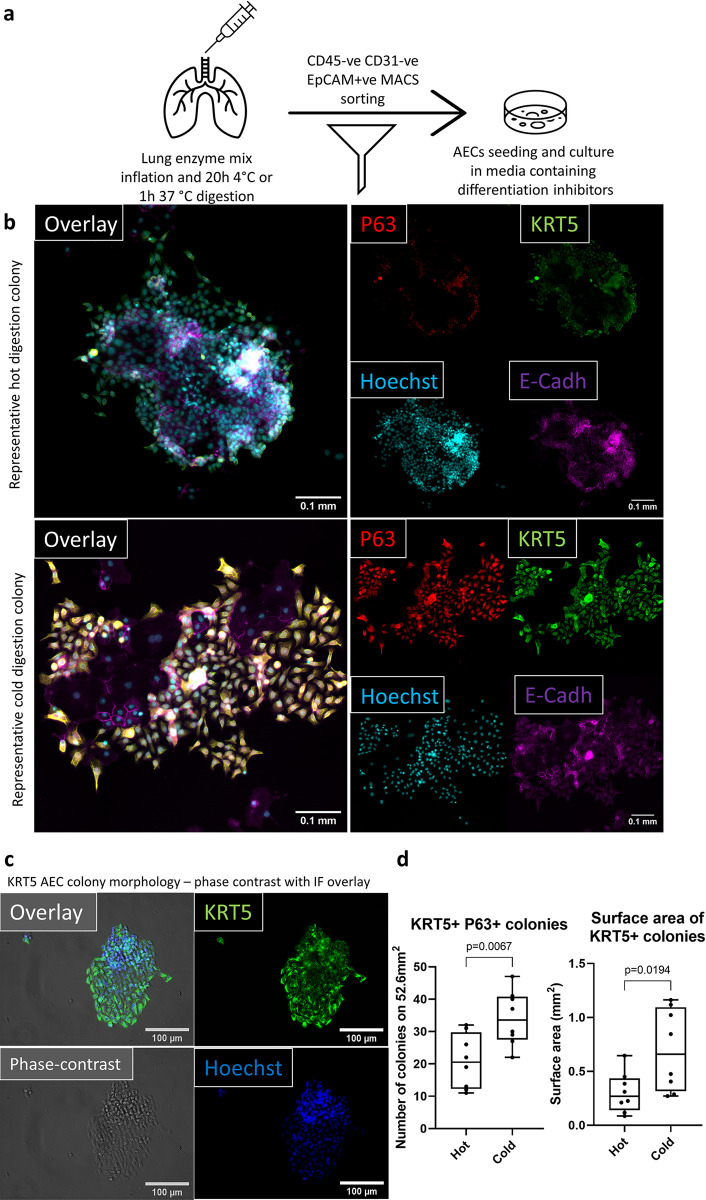
Fig 3. Improved AECs viability translates to a better performance in in vitro culture.
Cold digestion culture yields a greater number of basal cell colonies, which occupy a larger area. (a) Workflow diagram representing the steps involved in digesting the murine lungs and MACS sorting AECs for in vitro culture. (b) Representative immunofluorescent micrographs (cold and hot digestions) of P63 (red), KRT5 (green), Hoechst (blue) and E-Cadherin (magenta) used for quantification of the number of P63 and KRT5 double positive colonies. Scale bar 0.1mm. 25% of each 24-WP well imaged, which equals to area of 52.6mm2. Each well was imaged using 20x objective starting from the centre. (c) 20x magnification phase-contrast (grey) image overlayed with immunofluorescent KRT5 (green) and Hoechst (blue) images to present morphology of KRT5+ cells following cold digestion. Scale bar (white bar), 100μm (d) Quantification of the number (left) and surface area (right) of basal AECs colonies. Colony was defined as ten E-cadh/P63/KRT5+ cells in immediate vicinity. Colony numbers were quantified based on E-cadh/P63/KRT5+ cells, while colony surface was quantified using only KRT5 pixels. Unpaired t-test (n = 8), median ± min/max. Each data point is a single well cultured from MACS sorted CD45-CD31- EpCAM+ isolated from a single murine lung.