Figure 6. Loss of FtH1 in proximal renal tubules exacerbates ferroptosis and is associated with elevated tubular injury following glomerulonephritis.
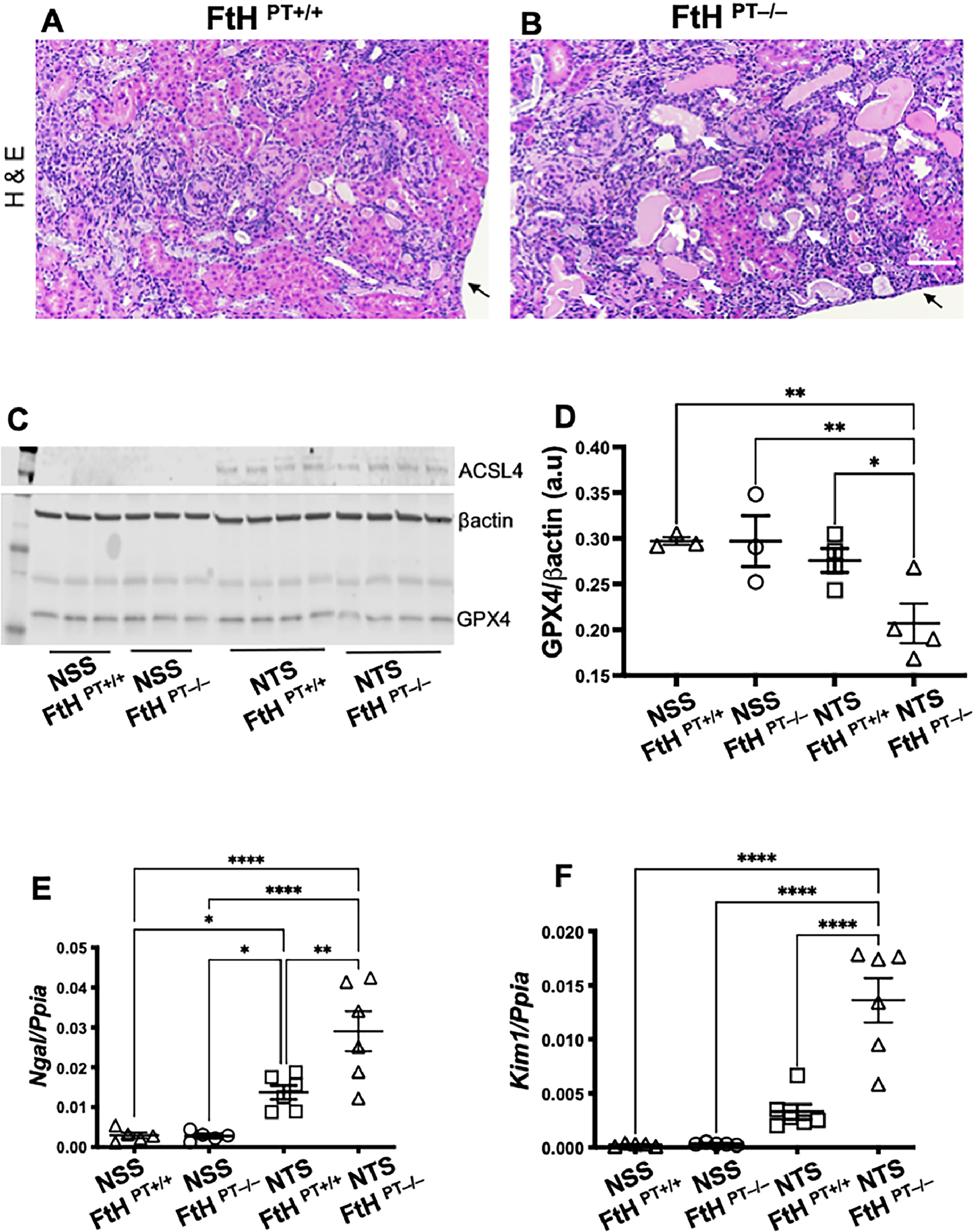
12-week-old female FtHPT−/− or FtHPT−/+ mice, were pre-sensitized with CFA (100ug), and four days later were injected i.v., with 100 uL normal sheep serum (NSS) or nephrotoxic sheep serum (NTS). Kidneys were analyzed 14 days later. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining revealed inflammatory infiltrates in both the groups (A-B). However, compared to nephrotoxic serum injected FtHPT+/+ mice (litter mate controls), FtHPT−/− mice had more tubular epithelial cell necrosis (dark pink fragmented cytoplasm with no nuclei) and denudation of the basement membrane (white arrows). Tubular casts, dilatation, luminal debris were also obvious in the FtHPT−/− (B) Arrow denotes end of the section. Scale bar = 100 uM. Normal sheep serum immunization did not elicit changes in ACSL4 and GPX4 in both FtHPT+/+ and FtHPT−/− mice (C-D). ACSL4 was upregulated comparably in nephrotoxic serum injected FtHPT+/+ and FtHPT−/− mice (C-D). However, GPX4 expression was lowest in the nephrotoxic serum injected FtHPT−/−. The observed renal pathology and exacerbated ferroptosis was supported by increased expression of proximal tubular injury markers Ngal (E) and Kim1 (F) in FtHPT−/− mice.
