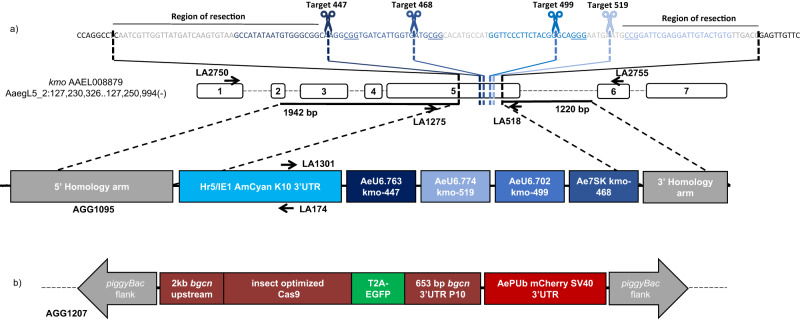
Fig. 1. Split-drive designs.
a Four sgRNA targets were selected within exon 5 of the kmo (AAEL008879) gene (dashed blue lines) of Ae. aegypti, disruption of which results in loss of pigmentation in the eye. The 135 bp region containing all four targets which is excluded from the plasmid (nucleotides between black dashed lines indicated in grey), is depicted above with the cut sites of each sgRNA indicated by scissors and blue text, PAM (protospacer-adjacent motif) sites are underlined. Note that cuts at any of the sgRNA target sites would require resection to reach perfect homology. Upstream and downstream regions were sequence confirmed in the Liverpool strain (WT) and the region of homology included in the plasmid is indicated by black bars. AGG1095 plasmid consists of an Hr5/IE1 (AcMNPV, ie1 promoter fused with homologous region 5 enhancer) expressing AmCyan (Anemonia majano cyan fluorescent protein) fluorescent marker, and four endogenous Ae. aegypti RNA pol III promoters each expressing the specified sgRNA. b The bgcn-Cas9 expression plasmid uses ~2 kb upstream sequence of the bgcn gene to express an insect codon optimized Cas9 followed by T2A-EGFP (2A peptide from foot-and-mouth-disease virus, enhanced green fluorescent protein) and the bgcn 3’UTR and an additional P10 3’UTR (Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus P10 3′UTR). A PUb-mCherry marker also contained within the piggyBac transposable element flanks allows for identification of transgenic mosquitoes. Individual elements are not to scale.