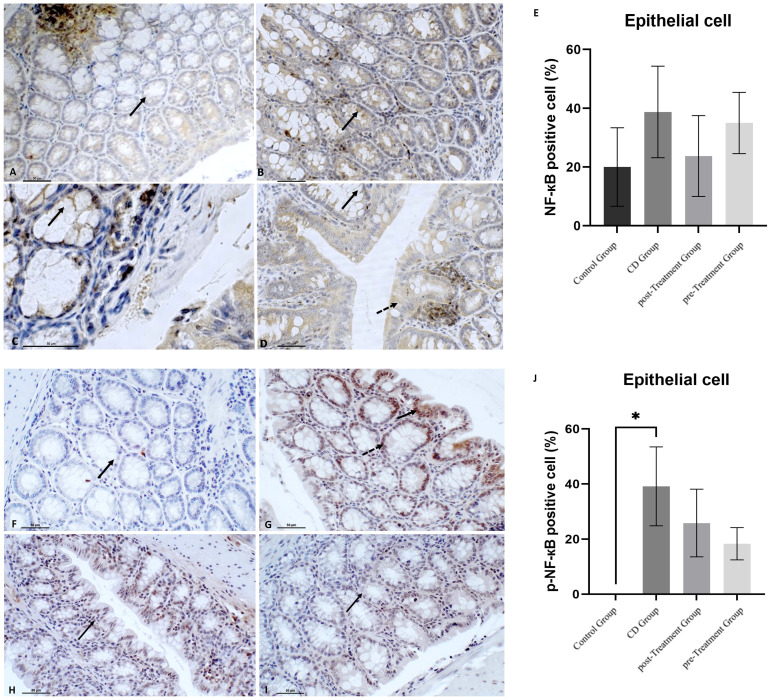
Figure 4.
Polyphenolic maqui extract shows preventing trend of decreasing NF-кB phosphorylation in colon epithelial cells from experimental animal model of Crohn’s disease-like colitis. Immuno‐histochemistry for NF-кB in colon from all groups (n= 6 mice/group): Immune+-NF-кB staining intensity in cytoplasm from crypts cells (black arrow) in (A) control group, (B) CD group, (C) post-Treatment group and (D) pre-Treatment group (D). Dashed arrow shows positive staining in colon epithelium in the pre-Treatment group (image D). Immuno‐histochemistry for p-NF-кB in colon from all groups: (F) Absence of staining of p-NF-кB in colons from control group (black arrow shows epithelial cell nucleus without positive staining for p-NF-кB), (G) Immune staining of p-NF-кB in crypts cells (black arrow) and in the epithelium (dashed arrow) in CD group, (H) Immune p-NF-кB staining intensity in cytoplasm from colon epithelium (black arrow) in the post-Treatment group (I) Immune p-NF-кB staining intensity in cytoplasm from crypts cells (black arrow) in the pre-Treatment group. (E, J) Percentage of positive cells (200x magnification) within representative areas for NF-кB and p-NF-кB expression in epithelial cells, respectively. Values represent mean ± SEM; *Different to the Control Group; p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s Multiple Comparison test.