Figure 1. Recombinant IgG1 cloned from single I-Ed tetramer-binding B cells preferentially bound to I-Ed–coated beads and B/c splenocytes.
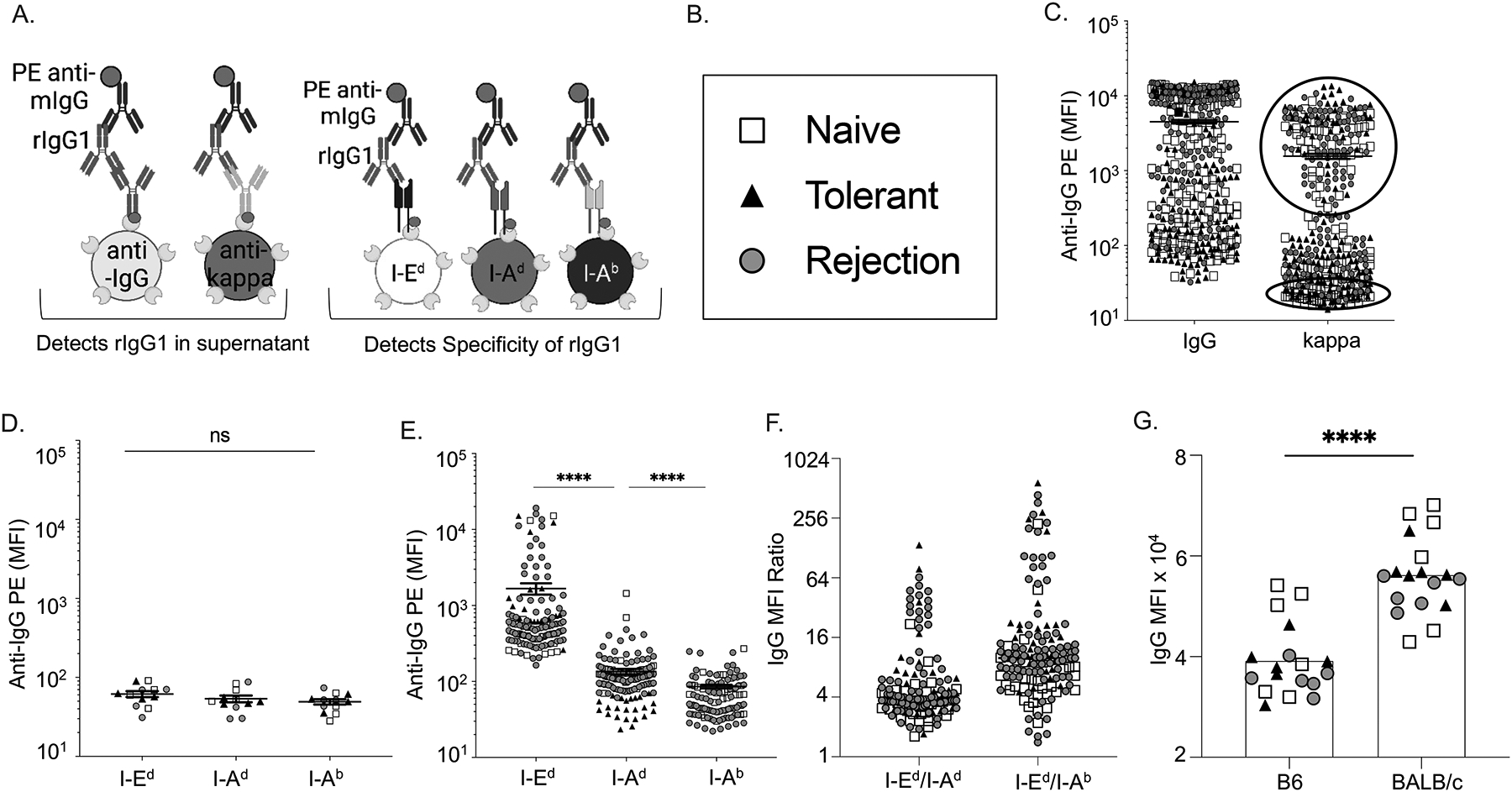
(A) Schematics of multiplex bead assay using streptavidin-coated beads displaying biotinylated anti-mouse IgG or anti-mouse kappa, and donor I-Ed, donor I-Ad or self I-Ab antigens. (C) Relative concentrations of mouse IgG1 and kappa in the culture supernatants of single BCR clones detected with PE-anti-IgG and presented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Each symbol represents one rIgG1 cloned from single B cells from naïve, rejecting or tolerant mice. (D-E) Supernatants with low (bottom circle 1C) or high (Top circle 1C) kappa concentrations binding to beads coated with I-Ed, I-Ad, or I-Ab, and presented as relative MFI. (F) Normalized MFI ratio confirms that rIgG1 expressed from I-Ed tetramer-binding B cells preferentially binds to I-Ed beads compared to I-Ad, or I-Ab. (G) rIgG1 binds to B/c B cells (CD19+) in the presence of blocking anti-CD16/32.
