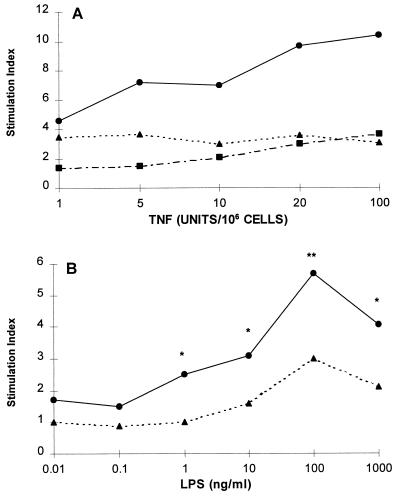
FIG. 2.
(A) Effects of varying TNF amounts on the LPS-induced CL response. Neutrophils were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of TNF or diluent for 20 min and then challenged with 1-μg/ml of LPS (E. coli K-235) or diluent for another 50 min. Neutrophils were treated with TNF only (▪), LPS only (▴), or TNF plus LPS (•). Results are the means of four duplicate experiments, expressed as stimulation indices. These were obtained by dividing the means of the treatments by the means of the baseline values. At all TNF doses, the effects of the combined action of TNF and LPS were significantly different from those of either agonist alone (P values of <0.0001 to <0.05 [analysis of variance]). (B) Response of TNF-primed neutrophils to varying concentrations of LPS (E. coli K-235). The cells were pretreated with 20 U of TNF/106 cells (•) or diluent (▴) for 20 min and then stimulated with the indicated concentrations of LPS. Values are stimulation indices. The data are the means of four experiments conducted in duplicate (∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01 [analysis of variance]).