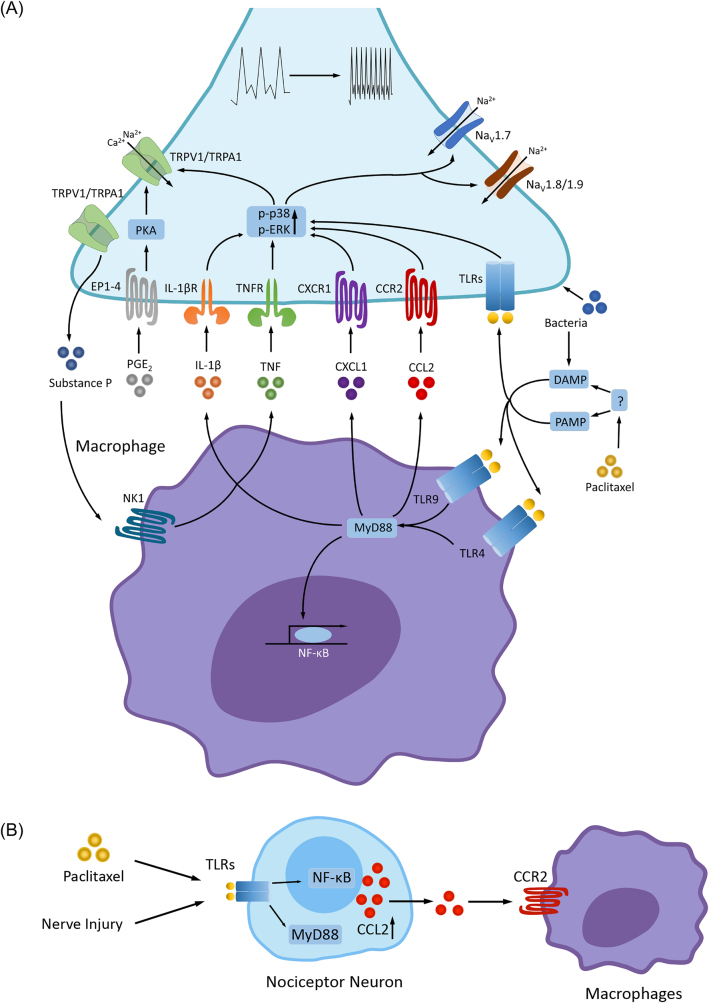
Figure 3:
Macrophages and induction of pain. (A) In macrophages, activation of TLRs (e.g., TLR4 and TLR9) by PAMPs and DAMPs [50] increases the synthesis and release of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (TNF, IL-1β, IL-17, CCL2, CXCL1) and lipid mediators (e.g., PGE2) via MyD88 and NF-κB pathways. PAMP and DAMP can be induced by bacterial and viral infections, tissues injury, or chemotherapy (e.g., paclitaxel). These inflammatory mediators act on their respective receptors (e.g., cytokine/chemokine receptors and EP1-EP4 receptors for PGE2) that are expressed on nociceptors [53, 54, 58, 59], leading to the receptor-mediated signaling transduction through phosphorylation of MAPKs (p-p38 and p-ERK) and activation of protein kinase A (PKA) [5, 60, 61]. Upon activation, these kinases then enhance the activities of ion channels (e.g., TRPA1/TRPV1 and voltage-gated sodium channels NaV1.7, NaV1.8 and NaV1.9) via posttranslational modulations, leading to increased sensitivity and excitability of nociceptors (peripheral sensitization) and increased pain sensitivity [62–64]. Bacteria is also known to produce pain via specific receptors and ion channels expressed by nociceptors [65]. Furthermore, activation of TRPA1/V1 in nociceptors releases substance P, which binds NK1 receptor on macrophages to release of TNF and IL-1β. In addition, nociceptor neurons express TLRs (e.g., TLR4 and TLR7), and activation of nociceptor TLRs by PAMP and DAMP (e.g., bacteria) can elicit pain. PAMP and DAMP can be indirectly generated by induction of chemotherapy. (B) After nerve injury and chemotherapy, nociceptor neurons produce CCL2 via activation of TLRs, MyD88 and NF-κB. CCL2 activates macrophages via CCR2 and induce macrophage infiltration in the DRG and nerve tissues [66–68]. CCL2, chemokine ligand 2; CCR2, chemokine ligand 2 receptor; DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern molecules; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecules; TLRs, toll-like receptors. Reproduced from Chen et al. [36] with CCC permission.