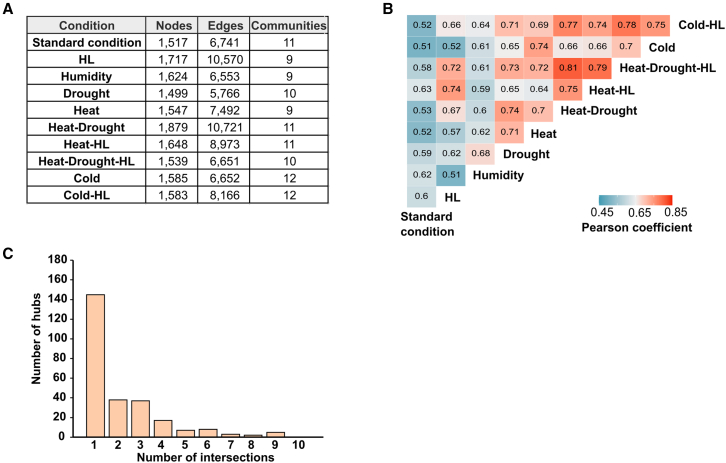
Figure 6.
Reconfiguration of metabolomes in Arabidopsis plants in different abiotic stress periods.
Compounds that changed in at least one treatment (P 0.05, linear mixed model, n = 5 independent experiments) were used to construct conditional networks (Supplemental Figure 7A).
(A) Network topological metrics in terms of size (number of nodes/metabolites), shape (number of edges), and detected communities (>20 nodes/metabolites) are shown.
(B) Comparison of global metabolome responses among abiotic stress treatments. Pearson correlations between the normalized node degree in each network were calculated to estimate (dis)similarities in the topology of the conditional networks.
(C) Commonalities in the local hub composition of networks. The three highest values for connectivity per community were considered to be local hubs and used for multiple comparisons (Supplemental Figure 7B). Bar plots depict the total number of common local hubs among treatments.