Figure 1.
Astrocyte-specific transgene expression by AAV carrying the astrocyte-specific mGfaABC1D promoter
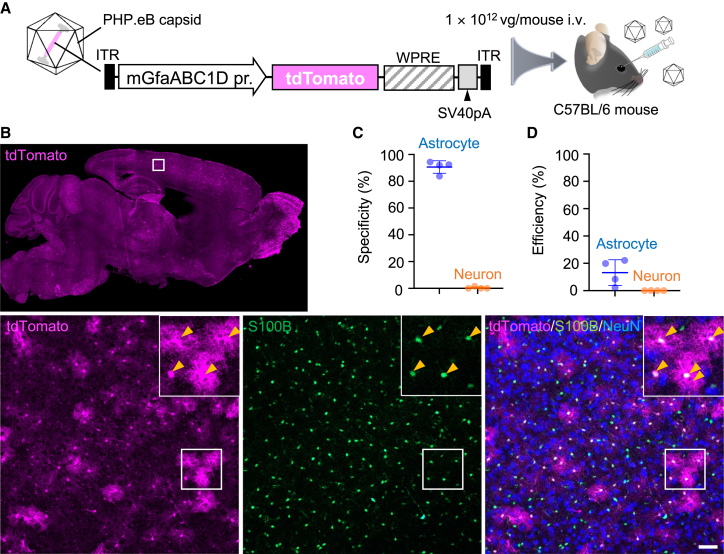
(A) Schema of AAV and experimental procedure. AAV vectors coated with PHP.eB, a BBB-penetrating capsid variant, which express tdTomato under control of the mouse GFAP (mGfaABC1D) promoter (100 μL, 1 × 1013 vg/mL), was injected into the C57BL/6 mouse through the orbital plexus. (B) Immunohistochemistry of mouse brain 3 weeks after AAV injection. Sagittal brain sections were immunostained for S100B, a marker of astrocytes, and NeuN, a marker of neurons. A square region in the tdTomato fluorescence image of sagittal brain section (top) was magnified (bottom), in which square regions were enlarged and presented at upper right corners. Arrowheads indicate S100B-labeled astrocytes. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Graph showing specificity for astrocyte transduction and that for neuronal transduction. Specificity for astrocyte (or neuron) transduction was calculated by the number of tdTomato and S100B (or NeuN) double-positive cells divided by the number of tdTomato+ cells. (D) Graph showing transduction efficiency for astrocytes and neurons. Transduction efficiency was calculated by dividing number of tdTomato and S100B (or NeuN) double-positive cells divided by number of S100B+ (or NeuN+) cells. Data (average ± SD) were obtained from 4 mice, and the value from each mouse was plotted. ITR; inverted terminal repeat; SV40pA; simian virus 40 polyadenylation signal.