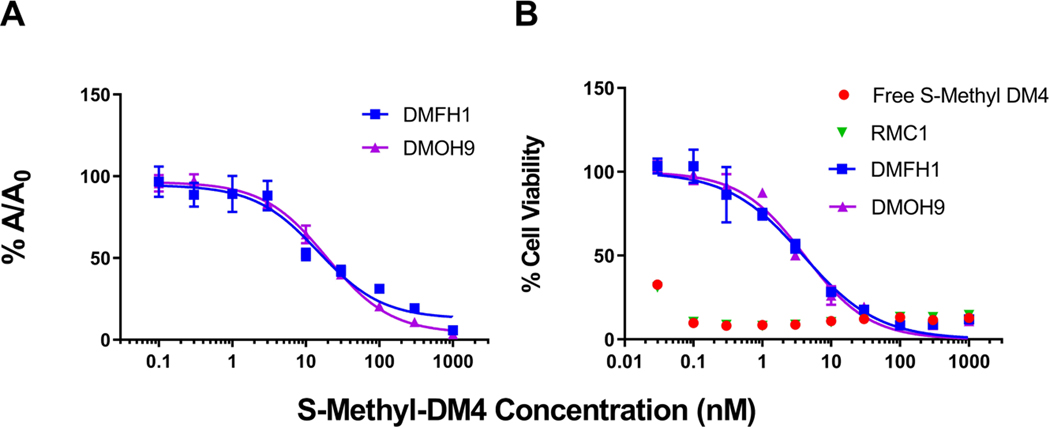
Figure 4. Binding evaluation of the anti-maytansinoid sdAbs to S-methyl-DM4.
(A) Affinity assessment of the sdAbs against S-methyl-DM4 was evaluated via competitive enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The concentration of each anti-DM4 sdAb was held constant, and free S-methyl-DM4 at concentrations ranging from 0.1 nM to 1 μM were added. Solutions were incubated for 30 minutes before being added to an ELISA plate coated with DM4-biotin-avidin. The fraction bound (%A/A0) of the sdAbs to immobilized DM4 decreased with increasing concentrations of free S-methyl-DM4. Points represent the mean of samples in triplicate with standard deviations depicted by the error bars. The two lead clones, DMFH1 and DMOH9, exhibit binding IC50 values to S-methyl-DM4 of 14.9 and 19.4 nM, respectively. (B) The lead anti-maytansinoid sdAbs potently inhibit S-methyl-DM4 cytotoxicity. SK-BR-3 cells were incubated with DM4 (30 pM – 1000 nM) with or without co-incubation with 10 μM of purified anti-maytansinoid sdAbs over a 24 h exposure period, following with viability assay to assess cell cytotoxicity. The results were normalized to cells treated with vehicle control and reported as % cell viability. The data was fitted for cytotoxic IC50 values with Hill slope in GraphPad Prism software. Each data point represents the mean of triplicate samples with standard deviations shown with error bars. The IC50 of S-methyl-DM4 applied to SK-BR-3 cells was less than 30 pM. In the presence of purified anti-DM4 sdAbs, DMFH1 and DMOH9, S-methyl-DM4 cytotoxicity was reduced more than 100-fold to IC50s of 3.93 nM and 4.10 nM, respectively.