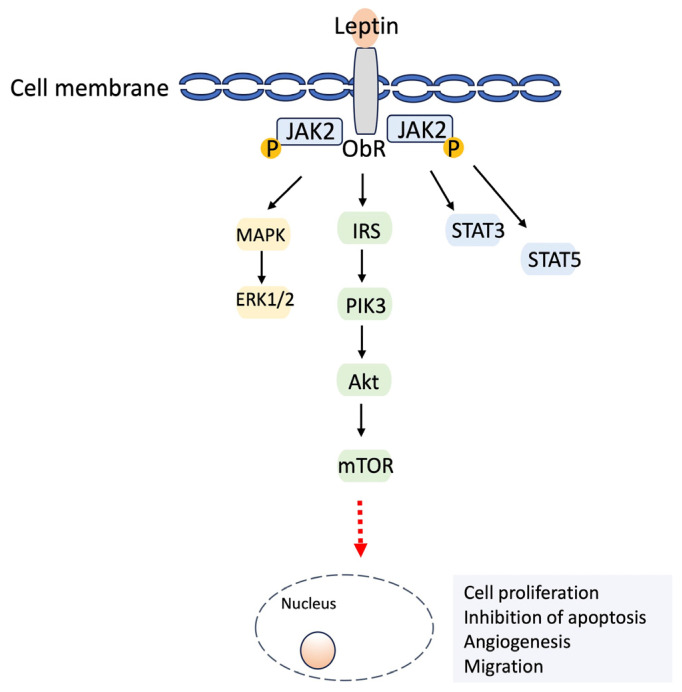
Figure 1.
A schematic illustration of leptin-induced signaling pathways. The binding of leptin to its receptor (ObR) leads to the formation of the ObR/JAK2 complex, which results in phosphorylation (P). This phosphorylation activates MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling, PI3K/Akt, and downstream signals such as mTOR. Also, phosphorylated STAT3 and STAT5 translocated to the nucleus activate target genes. This leptin-induced signaling pathway promotes cell proliferation, inhibits apoptosis, and facilitates angiogenesis and migration.