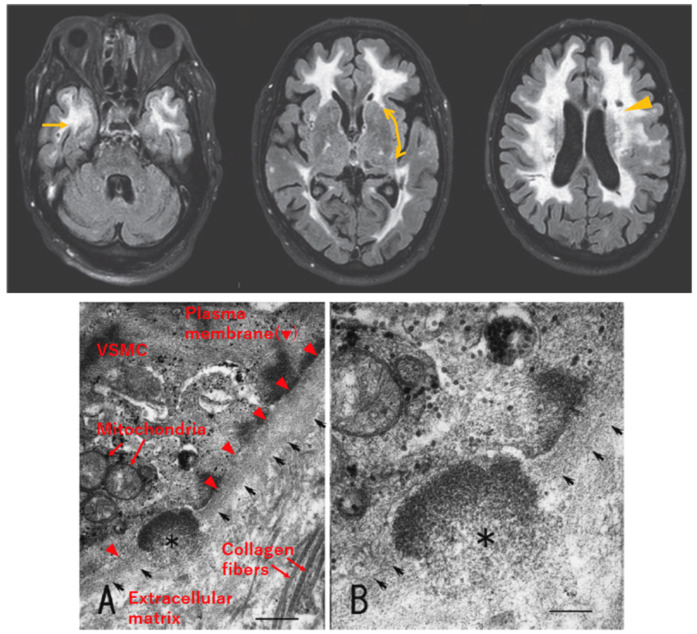
Figure 2.
Radiological and pathological characteristics of CADASIL. Upper: Axial section of fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) MRI of a patient with CADASIL, reproduced with permission from Mizuno, 2012 [17], published by the Japanese Society of Neurology, with slight modification. White matter lesions are detected as hyperintense areas in deep white matter, including the temporal pole (left, arrow) and external capsule (middle, bidirectional arrow, faint signal in this patient). Lacunar infarcts are detected as punctiform low-intensity lesions (right, arrowhead). Lower: Electron micrograph of skin biopsy specimen, reproduced with permission from Mizuno et al., 2008 [18], published by the Japanese Society of Internal Medicine, with slight modification. Granular osmiophilic material (GOM, asterisk) exists within the basement membrane (arrows) of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Labeling of cellular structures is presented in red in (A). Scale bar indicates 410 nm in (A) and 200 nm in (B).